Understanding the attitudes of Thai students in Sweden toward recycling system A study of container deposit system.
Master Thesis (EFO705): MIMA - International Marketing Authors (Group 2495): Jittranuch Lertchaiworakul (841002)
Songsathit Lorgunpai (830812) Supervisor: Tobias Eltebrandt
Examiner: Ole Liljefors
School of Sustainable Development of Society and Technology (HST)
Abstract
Date: May 28, 2010
Program: MIMA-International Marketing
Authors: Songsathit Lorgunpai Jittranuch Lertchaiworakul
Title: Understanding the attitude of Thai students in Sweden toward recycling system: a study of container deposit system.
Problem: -What differences can be observed in attitudes of Thai students in Sweden toward recycling and container deposit system before came to Sweden and after they come?
-In what ways Thai students’ behave on the recycling system and new innovation – container deposit system?
-What are reasons that Thai students in Sweden use container deposit system?
Purpose: The authors study the attitude of Thai students who are studying in Sweden toward recycling and container deposit system by comparing the level of attitude before they came to Sweden and after they come to Sweden in order to understand the differences and the changing attitude. The result of this research will be beneficial for the government and related organization to further study and use as a guide to creating the project plan concerning the recycling and container deposit system.
Method: The attitude and the acceptance of the innovation were applied at different aspects to analyze the 100 sample size. We use questionnaire survey through internet base to collect the data for primary data. And we search from the internet, article, journal and news which related to recycle system and container deposit system for secondary data.
Conclusion: The differences of age have no different attitudes toward recycling and container deposit system. The majority of respondents have changed their attitude toward recycling and container deposit system in the positive way after they come to Sweden.
Recommendations: In order to do a further study based on this paper, numbers of
respondents should be concerned. Also, providing the knowledge and education in terms of recycling is one of the factors that influence the attitude to the positive way.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction ... 1 1.1 Background ... 2 Thailand ... 2 Sweden ... 2 1.2 Strategic Question: ... 3 1.3 Research Question: ... 3 1.4 Objective ... 31.5 Scope of the research ... 4
1.6 Target Audience ... 4
2. Methodology ... 5
2.1 Topic selection ... 5
2.2 The development of framework ... 6
2.3 Research Method ... 6
2.3.1 Data collection ... 6
1.) Primary Data ... 6
2.) Questionnaire Design ... 7
3.) Questionnaire design and Questionnaire structure ... 9
4.) Secondary Data ... 10
2.4 Scope of study and delimitation ... 10
3. Theoretical Framework ... 11
3.1 Innovation ... 11
New Product buying – Criteria for Acceptance of Innovation ... 11
3.2 Diffusion of innovation ... 12
3.3 Attitudes ... 13
The concept of attitudes ... 13
The triadic model of attitudes ... 13
Measuring Attitudes ... 14
Attitudes and Behavior ... 14
The dynamics of attitude change ... 14
3.4 Theory of reasoned action ... 15
3.5 Conceptual Framework model ... 16
4. Findings ... 18
4.1.1 Benefits of Recycling ... 18
4.1.2 Recycling system and container deposit system in Thailand ... 18
4.1.3 Container deposit system in European countries ... 20
4.2 Primary Findings ... 23
4.2.1 Questionnaire Part1: Demographic (Questions 1-3) ... 23
4.2.2 Questionnaire Part2 (A): Knowledge (Questions 5-8 and 24-27) ... 24
4.2.3 Questionnaire Part2 (B): Attitude (From choice 9-21 and 28-40) ... 27
4.2.4 Questionnaire Part2 (C): Behavior (From choice 22-23 and 41-42) ... 33
4.2.5 Questionnaire Part2 (D): The reason of acceptance ... 36
4.2.6 Questionnaire Part3: The reasons why people use container deposit system. ... 39
5. Analysis ... 41
5.1 The knowledge ... 41
5.2 The attitude ... 42
5.3 Innovation Acceptance ... 43
The criteria of innovation... 43
Innovation acceptance ... 44
5.4 The reason to use container deposit system ... 45
6. Conclusion ... 46
7. Recommendation ... 47
8. Reference Lists ... 48
9. Appendix Part ... 52
Appendix I: QUESTIONNAIRE (English Version) ... 52
Table of Figure
Figure 1: Model of the five stages in the innovation decision process (Roger, 1995) ... 13
Figure 2: Theory of the action model (Ajzen,1991) ... 15
Figure 3: Conceptual Framework ... 16
Figure 4: 2006 & 2005 results of packaging collection ... 21
Figure 5: Recycle rate and amount of deposit ... 22
Figure 6: Gender ... 23
Figure 7 Age ... 23
Figure 8: Lastest education level... 24
Figure 9: The idea about recycling and container deposit system ... 24
Figure 10 Comparison level of knowledge about recycling between female and male ... 25
Figure 11: Comparing level of knowledge about benefits of recycling between male and female ... 25
Figure 12: Comparison level of knowledge about Container deposit system (CDS) between female and male ... 26
Figure 13: Comparison the attitude toward recycling and container deposit system ... 27
Figure 14: Comparison the importance of recycling between female and male ... 28
Figure 15: Comparison concerning of recycling between female and male ... 29
Figure 16: Comparison the attitude that CDS can reduce the waste between female and male ... 29
Figure 17: the attitude that CDS can reduce the waste between female and male... 30
Figure 18: Comparison behavior of sorting waste between female and male ... 31
Figure 19: Comparison behavior of sorting waste even no recycle around there... 31
Figure 20: Comparison attitude that CDS can reduce energy ... 32
Figure 21: Can and PET purchasing frequency ... 33
Figure 22: number of respondents who thrown can and PET into the recycle bin. ... 33
Figure 23: Purchasing Frequency and percentage of recycle BEFORE came to Sweden ... 34
Figure 24: Purchasing Frequency and percentage of recycle AFTER come to Sweden. ... 35
Figure 25: Attitude toward return the container to machine is wasting time. ... 36
Figure 27: Attitude toward CDS affects buying behavior ... 37
Figure 28: Attitude toward inconvenience to return empty bottle at machine ... 37
Figure 29: Attitude toward container deposit system is complicate to use ... 38
Figure 30: Number of respondents who thrown can and PET into the recycle bin... 39
1
1. Introduction
Now a day environmental concern is becoming a critical issue because a variety of problems affect to the entire world especially ways of human life. Some organizations or government have been encouraged people to aware of the environmental impact. Most of developed countries such as United States of America, European countries like Denmark, Sweden or Norway which have already responded to this crucial issue by encourage their citizen to recycle the disposal including implementing the container deposit system (bbc.co.uk).
A container deposit refers to a deposit on beverage container that are collected from distributors and retailers when the beverage are sold, for example, a bottle of water, soft drink or alcohol beverage. Retailers collect deposit from consumer at the point of purchase. The deposit will be refunded to consumer when the container beverages are returned at the authorized redemption center (container-legislation.org).
According to the Pollution Control Department in Thailand, the number of solid wastes has been rapidly increased due to the increasing population, tourism support and economical recovery. In 2005, Thailand approximately has 40,000 tons of refuse disposals per day. Almost 9,000 tons are from Bangkok (Pollution Control Department, 2004). Furthermore, Thailand does not have legislation concerning deposit system before. Therefore, it is a good opportunity for us to study regarding this issue. Due to the current waste problem, Thailand should reduce the solid waste by having a policy of waste management especially on recycling system, for example, implementing the container deposit system in order to save the environment, shape Thai people’s behavior on recycling things and also responsible for the package waste.
From this research, we will explore the attitudes of Thai student in Sweden toward recycling and container deposit system whether they have positive, neutral or negative attitude. In addition, we will study on the acceptance of the new innovation of this group.
The author found that this study can be beneficial for people in the Thailand as well as it could enhance our environment.
2
1.1
BackgroundThis chapter provides the information about recycling and waste management system in Thailand and Sweden. The reason why we show Thailand and Sweden fact is because our respondents are Thai student who are studying in Sweden. Therefore, comparing the fact between two countries will help the reader to understand the background.
Thailand
The number of disposal in Thailand has been gradually increased year after year. However, in 2005, the amount of waste in Thailand has reached 14.3 million tons which decrease 0.3 million tons from the previous year because of the waste management policy which issued by Bangkok Metropolitan Administration (Pollution Control Department, 2004). However, the number was still very high for government to manage. According to the Department of alternative Energy Development and Efficiency (DEDE), Thailand has a proper method of refuse disposals just only in Bangkok district. From 70-85% of the waste which can be collected, just only 30% are managed well (DEDE). In particular, Thai people are familiar with using plastic bag which take hundreds of years to decompose. Therefore, the rest that can’t be managed will cause a serious pollution problem and effect to the people who live near that area. Nevertheless, the department of environmental quality promotion put concern on this issue by cooperating with supermarket and department store to launch “reduce plastic bag usage campaign” which encourage Thai people to reduce the plastic bag usage (thaienv.com).
Sweden
In 1947, Swedish waste management was founded and Swedish government has passed the bill “Recovery and management of waste” which resulted in support for up to 50% of the capital cost of plants for the recovery and other utilization of domestic waste (waste management and research, 1985). Until now, the Swedish statistic shows a great number of changes in waste management over past ten years. In 2007, the amount of household waste increased by 4.8% to 4,717,380 tons from the previous year. However, Sweden has a good waste management system. The statistic shows that 48.7% went to recycling while 46.4% for waste incineration with energy recovery (avfallsverige.se). In terms of container deposit system in Sweden, nearly all containers, for example, aluminum and PET (Poly Ethylene Terephthala) for consumption are deposited. 91% and 88% are returned respectively which
3
means the high number return (pantamera.nu). Also, there are total circulations of around 130 million bottles and each bottle has been used for 40 times (sverigesbryggerrier.se).
According to Fisher, the strategic question cannot be answered by doing research because it concerns the future and we cannot research something that has not yet happened. On the other hands, research question is the question that researcher can do a research, study and at the end answer the question (Fisher, 2007).
1.2
Strategic Question:“How would Thai students accept the container deposit system?”
1.3
Research Question: “What differences can be observed in attitudes of Thai students in Sweden toward recycling and container deposit system before came to Sweden and after they come?”
“In what ways Thai students’ behave on the recycling system and new innovation – container deposit system”
“What are reasons that Thai students in Sweden use container deposit system?”
1.4
ObjectiveThe objective of this study is to learn Thai students’ attitude in Sweden toward recycling and container deposit system. In terms of recycling, Thailand still needs to be developed and require better collaboration from every organization as well as Thai people. Even though there are some recycling campaigns which are successful, for example, a campaign from Nokia which encourage Thai people to recycle mobile or mobile battery and have a chance to receive the new mobile phone (siamphone.com). Besides, the deposit system has never been established. Since the authors are the students in Sweden. We have found that Sweden manage the recycling system quite well. According to waste Sweden, in 2005, the material were recycled 34% of household waste and in 2010, the rate will reach 50% (avfallsverige.se). It means that Swedish people give an important to the recycling. Therefore,
4
it is a good opportunity to study the attitudes of Thai student who are studying in Sweden whether they has changed the attitude of recycling after they come to Sweden or not.
At first, we will study the attitudes and their changing habits over Thai students in Sweden before came to Sweden and while living in Sweden. Then we can learn from this group comparing to the potential of Thai people toward recycling and container deposit system.
The ultimate goal is to study how much Thai people accept the container deposit system.
1.5
Scope of the researchThe scope of this research was limited to study the attitudes of Thai students in Sweden toward recycling and container deposit system. The main is to be focused on the attitudes before they came to Sweden and after they come to Sweden whether they have changed their attitude or not. Moreover, some facts about recycling and container deposit system will be used as the supported information for this research.
1.6
Target AudienceThis study can be beneficial for Thai people as well as Thai government. Understanding Thai students’ attitude in Sweden toward recycling can be useful for the government or the related organization to start establish the recycling system which will be resulted in improving standard of living toward Thai people as well as saving the environment.
5
2. Methodology
In this chapter, we discuss the research method by introducing the area of topic selection that places our interest. Then we studied the articles and theories which relevant to the problem. After that, we selected the method of data collection including both primary and secondary data, population and sample selection, considering upon possibilities and time limitation. Once we conducted all the useful data, we analyze the data with the relevant theories.
2.1
Topic selectionAs the authors are studying in Sweden and we found out that Swedish people are quite environmental friendly. Authors notice a recycling sign on every bin and there are specific bin for specific type of garbage. This can show that Swedish people give an important to recycling system and they have environmental friendly behavior. We also found that container deposit in Sweden is quite interesting and successful system to encourage people to return recycling container such as aluminum can, Poly Ethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Glass bottle. In addition, due to the increasing global environmental awareness, this system will help the recycling process and save the world environment. Therefore, we found it interesting if Container deposit system can be implemented in Thailand which will not only save the environment but also persuade Thai people to have responsibility to recycle the waste. Firstly, we start studying about attitude from Thai students in Sweden – on recycling system and container deposit system in Sweden. More over we study on how Thai student accepting the innovation especially on container deposit, which is an advance technology and innovative for Thai people. The reason why we choose Thailand as the target is because 80-95% of the waste in Thailand can be recycled but people don’t put any concern regarding recycle (mtec.or.th)
As a result, the attitude from Thai students in Sweden toward container deposit system was demonstrated and also the acceptance on the container system as well. The outcome can be useful for environmental organization, recycling manufacturer and related industry.
6
2.2
The development of frameworkFirstly, we searched the information by finding the articles, news or journals relevant to the topic in order to broaden the idea and authors’ perspective. We found some useful articles which discussed about the container deposit legislation in several countries, some advantages as well as disadvantages, the supporters and the obstacles. The keywords for searching are “container deposit”, “the attitude”, “the acceptance”, “innovation” and “the bottle bill” for example.
Secondly, we studied the theory which can be supported and relevant to the topic. We then searched from the academic journals, database and the previous research from DIVA database, Emerald database including several text books and online.
2.3
Research MethodTo study the attitudes of Thai students toward container deposit system and recycling system, we decided to conduct data from two sources which are primary data and secondary data.
2.3.1 Data collection
1.) Primary Data
Primary data is data that you collect by yourself and this data is specific for your problem and your research. Primary data can be both qualitative data which usually are word and quantitative data which usually in form of number. To collect the primary, it can be done in several ways such as questionnaire, interview and focus group. (Thames Valley University, n.d.)
In this paper, we used survey method to collect the data by tailor the questionnaire to answer the research question and to find the innovative acceptance from respondents, Thai students in Sweden.
Internet (Webpage) survey is the way we selected to distribute the questionnaire. In order to easily reach people in many place by using internet as a medium. High speed of access by just use e-mail and sent to respondent. Another benefit of using internet survey is low cost and some survey online provide internet survey for free. Surveyor can save printing cost and
7
travelling cost. Moreover the advantage of using internet base questionnaire is the software operates the data and presents it properly. (The survey system, n.d.)
As authors is studying in Sweden while there are Thai student live in nationwide especially in Stockholm, Karlstad, Uppsala, Gothenburg and Lund, internet is the suitable way access to these popularity.
Our main respondents are Thai students in Sweden to find out their attitude about container deposit system before they came to Sweden and the attitude about the system after they live in Sweden. The reason why we chose Thai students in Sweden is because in Thai student in Sweden has an experience on pre using and post using the recycling system. We will use email as a channel to distribute the questionnaire and we expect 100 respondents back.
2.) Questionnaire Design
“Keep the questionnaire as short as possible. Two or four side of A4 paper would be good for research for a Master dissertation” (Fisher, 2007, P.192)
“Give it a logical and sequential structure so that the respondent can easily see what the question is about and can follow its themes as they develop” (Fisher, 2007, P.192)
“Ask the easy question first and the hard ones last” (Fisher, 2007, P.192)
According to the “Researching and Writing a Dissertation” mentioned statement above, The questionnaire was in 4 parts which are 1.General information, 2.Attitude toward recycling system and container deposit before they came to Sweden, 3.Attitude toward recycle system and container deposit after they come to Sweden and the last part is to find the reasons of acceptance the container deposit system. And as the main purpose is to study about Thai student’s attitude so author create questionnaire in Thai.
Authors selected several different formats of question in questionnaire survey to collect data.
Dichotomous question “There are questions that offer the respondent only two alternatives” (Fisher, 2007, P.193) Authors use dichotomous question to ask about simple and clear question.
For example: What is your gender? __Male __Female
8
Multiple Choices “These questions normally provide respondents with a choice of three to five options and ask them to choose one” (Fisher, 2007, P.193). This type of question was used in order to collect information about their general data and behavior. Respondents can answer clearly.
For example: What is the respondent age?
__18-23 __24-27 __28-30 __Over 30
How much do you buy aluminum can?
__less than 7 units / week __8-14 units / week __15-21 units / week __ More than 21 units / week
Likert Scale was used to measure the attitude of people on the statement provided whether they agree or disagree (Fisher, 2007, Page 195). Basically, five point scale between strongly agree and strongly disagree be used. However, in this questionnaire, authors use even point scale to force respondent to choose whether they agree or disagree by design to 6 point scale, 1 is strongly disagree to 6 strongly agree. (Likert Scale, 2006).
For example: Do you agree with this statement?
I think container deposit system is 1 2 3 4 5 6 an efficient way to recycling
Rating Scales was used to rate or evaluate an option provided (Fisher, 2009, P194). In this questionnaire, we use 5 scale rates to measure the knowledge about recycling system which 1 is the least and 5 is the most.
For example:
Before come to Sweden, How much 1 2 3 4 5
9
3.) Questionnaire design and Questionnaire structure
According to the main purpose of this paper is to study the attitude of Thai student in Sweden toward recycling system, the questionnaire was created to follow conceptual framework.
The questionnaire design related to conceptual framework as following;
Section Example of Question Conceptual
Framework
Number of Question
General Information Gender, Age, Education,
General information Questions 1-4
Attitude BEFORE came to Sweden Knowledge about recycling and Container Deposit system Diffusion of Innovation Questions 5-8 Attitude toward recycling and Container Deposit system Reasoned of Action and Attitude Questions 9-11, 13, 15, 16, 21
Attitude AFTER come to Sweden Knowledge about recycling and Container Deposit system Diffusion of Innovation Question 19, 24-27, 38 Attitude toward recycling and Container Deposit system Reasoned of Action and Attitude Questions 28-30, 32, 34, 35, 40 The reason of acceptance
The reason why respondent use redemption machine Criteria for Acceptance innovation Questions 12, 14, 17-18, 20, 31, 33, 36, 37, 39 , 43 -47
Behavior The buying frequency
of PET and aluminum can Criteria for Acceptance innovation Questions 22-23, 41-42
10
4.) Secondary Data
The authors divided secondary data into 3 parts; the benefits of recycling, some facts about recycling system in Thailand and the container deposit system in European countries. The purpose of this secondary data is to show the readers to get the overview of the current situation. We collected secondary data from many sources such as the university library’s database, for example, Emerald and DiVA. Also we obtained some information from online such as web based survey internet.
2.4
Scope of study and delimitationThis paper focuses on Thai students in Sweden and study their behavior and attitude toward recycling system and container deposit system while studying the possibility to implement “Container Deposit” system in Thailand.
Due to the time limitation and the distribution of questionnaire, so we will use e-survey by sending the questionnaire through e-mail and wait for their response. Spreading e-mail is the quickest way to get the response because the authors live in Västerås, Sweden during conducting the research while the respondents are Thai student in Sweden, they might study in other place in Sweden that conductor cannot reach. Moreover, our sample will be all Thai students in Sweden who live in Sweden no longer than 2 years.
The reason why we focus on Thai students who have been living in Sweden no longer than 2 years is because the authors intend to study about the attitude toward recycling system and container deposit system and compare the differences while they had been living in Thailand which its recycling system is not quite efficiency and during they live in Sweden, a successful country in recycle system. If the respondents stay in Sweden long time, their attitude might change to fit with Swedish culture and norm and they might not able to remember what is their attitude about recycle system since they live in Thailand which can make this survey inefficiency.
11
3. Theoretical Framework
3.1
InnovationAn innovation is defined as the new creativity things which person can be perceived. It is anything (e.g. idea, concept, product or service) in the marketplace (Evan, Jamal and Foxall, 2006) and it is perceived differently by individual or other unit of adoption (Rogers, 1983).
New Product buying – Criteria for Acceptance of Innovation
In “Consumer Behavior” (Evan, Jamal and Foxall, 2006), the author discussed about criteria that make people accept on the innovation and new technology which might determine the successful of launching new product or new system. There was 10 criteria mentioned following
Compatibility is about how the innovation related to people’s current value, cognition and value. How much people have to change and adapt to fit with the new innovation. As much as people have to change is less chance for people to accept it.
Relative advantage: the degree to show how the advantage that the product has. This is might the most influence criteria for acceptance because people always concern for the advantage that they got from the product.
Trialability: the product allowed customer to try on it to see how it works while to learn about the product without taking any risk.
Observability: the product was used by other customer or can easily found in public. This situation might influence customer to see the effect of the product from other user and it can support customer to make decision easier.
Speed: this show how fast those customers get benefit from applies for the innovation. Faster benefits go back to customer, easier for customer to decide to accept the product.
Simplicity: the product is simply and easy for customer to use and try. It does not require high effort to learning and use it.
12
Perceived Risk: if the perceived risk of the new innovation is low, it is easier for customer to adapt themselves to use the product. In opposite way, customer might feel unsecure on product that has to put a lot of effort or money on it.
Product Symbolism: it can be inferred that how product means to the customer and reflex to an “image” to the user. If the product reflex a positive image and means to the customer, it will be easy for the customer to accept this innovation.
Aesthetic or Hedonistic Innovation: the appearance and feature is the important for them and influence the customer to accept or decline the innovations.
Innovation Overload: this part can be referred in case of the customer face so many new products in the short period of time. It will make customer overload with innovation and stop learning or accept new product.
3.2
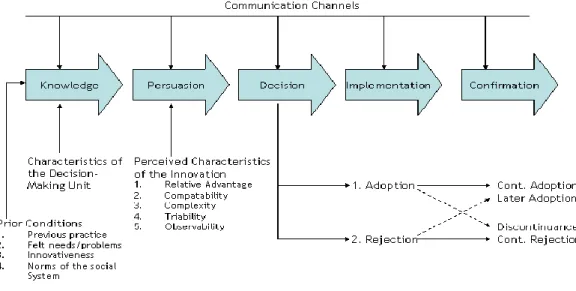
Diffusion of innovationDiffusion is the process by which an innovation is communicated through certain channel overtime among the members of a social system (Roger, 1983). The diffusion of innovation consists of innovation, communication channel, time and social systems. Rogers stated that people concern how a new product is accepted or not and they will continue using it or not depend on the following 5-step decision process.
(1) Knowledge – person aware of the innovation and how to use it.
(2) Persuasion – person has the positive or negative towards the innovation.
(3) Decision – it occurs when a person do the activities which leads to adopt or reject that innovation.
(4) Implementation – person use the innovation.
(5) Confirmation – it is an evaluation the results of the innovation.
These 5-step processes are made when people perceive the innovation. There are various reasons why people adopt the innovation which depends on individual and social system. They will consider the utility and the benefit they have got, the consideration in costs and also function of the innovation (Greg Orr, 2003). However, we will only use first three steps which are knowledge, persuasion and decision to analyze in the research because the purpose
13
of this research is to study the attitudes of the innovation until whether they will accept or reject the innovation.
Figure 1: Model of the five stages in the innovation decision process (Roger, 1995)
3.3
AttitudesAn attitude is what individual sees, views or thinks toward a person or certain object. It could be positive or negative based on their experience and learning. Loudon and Della Bitta defines attitude as “an enduring organization of motivational, emotional, perceptual and cognitive process with respect to some aspects of the individual’s world” (Evan, Jamal and Foxall, 2006). Back in 1918 Thomas and Znaniecki described attitude as a state of mind of the individual toward an object. Later on in 1954, Gordon Allport proposed the most famous definition of attitudes is that attitude is a learned predisposition to think, feel and behave toward a person (or object) in a particular way (Erwin, 2001).
The concept of attitudes
The triadic model of attitudes
Attitudes consist of three components; Affect, Behavior and cognitive. Affect is an emotional content of attitude. It can be seen as positive or negative. Cognitive is a combination of person’s beliefs and knowledge about an issue or an object. Behavior is what individual
14
response or a tendency to behave in a certain way. These three components formed attitudes (Carlson, Buskist and Martin, 2000).
Measuring Attitudes
According to Erwin, there are numbers of methods that can measure attitudes. Each one has both advantage and disadvantage. However, choosing a method depends on the issue under investigation or population concerned, for example, a survey or standardized attitudes scale are an ideal solution for measuring attitudes of a large population to some relatively innocuous while measuring sensitive issue, you need to use more subtle or indirect technique such as projective test in order to avoid the fake attitudes (Erwin,2001).
Attitudes and Behavior
“People do not always behave as their expressed attitudes and beliefs would lead us to expect” (Carlson, Buskist and Martin, 2000). The relationship between attitudes and behavior has been a critical issue for long. Many theorists believe that attitudes and behavior are closely related while Wicker stated that there was a poor link between attitudes and behavior (Erwin, 2001). However, there are some factors such as individual and situational constraints that must be taken into consideration when measuring this particular issue. Besides, the constructs are measured at different level of specificity (Ajzen and fishbein, 1980). The attitudes assessed are in general evaluation whereas behaviors are specific toward a particular person. However, as the attitudes that we measure becoming more specific, the person’s behavior becomes more predictable (Carlson, Buskist and Martin, 2000).
Fazio and Zenna also stated that the relationship between attitudes and behavior can occur strongly where attitudes have been acquired through direct experience (Erwin, 2001).
The dynamics of attitude change
In fact, the changing in attitude can be occurred by many reasons. According to Ross and Sacker, the changes in attitudes are considered to be the result of three processes; general replacement, life cycle and period effects. General replacement occurs in the level of nation, in the attitude of old people, not in an individual. Period effect is one type of intra-individual change. It is a result of the context in which people are living. Lastly, life cycle is the changing though the age of person’s lifetime (Ross and Sacker, 1983).
15
In terms of another perspective, it is believed that changing attitude can be occurred because of consistency concerns. One of the most famous theories describing this issue is cognitive dissonance. Festinger (1957) believes that cognitive dissonance is the state of discomfort. It is a feeling that encounters two conflict situations between attitude and behavior. Creating additional reasons will occur in order to support another choice. Changing attitude is the way to reduce individual dissonance. It is believed that dissonance can be applied to all situation involving attitude formation and change (Festinger and Carlsmith, 1959).
3.4
Theory of reasoned actionThe theory of reasoned action firstly was described by Fishbein and Ajzen. This theory studied to understand the motivation influenced on behavior and the most important factor of person’s behavior is intent. The behavior intent, intention to perform behavior is the form of attitude and subjective norm. According to the theory can say that if person intent to do a behavior then it is likely that person will do it. If the attitude on the outcome of performs a behavior is positive and the subjective norm said it is positive, and then the person will perform a behavior volitionally. (Fishbein & Ajzen, 1975)
It is described as the model below
Figure 2: Theory of the action model (Ajzen,1991)
Attitude
Subjective Norms
16
3.5
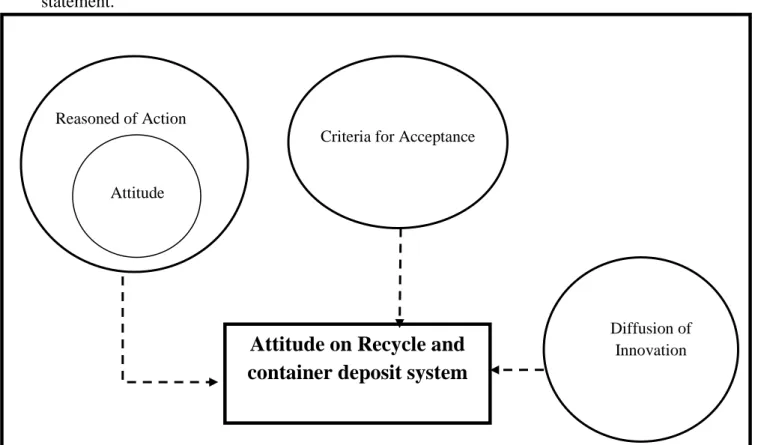
Conceptual Framework modelThis part demonstrates the relationship and the linkage of concept to describe the problem statement.
Figure 3: Conceptual Framework
Source: Model developed by the authors.
This above framework shows the connection to the attitudes of Thai students in Sweden toward recycling and container deposit system. The reasoned of action illustrates the action which lead to the reason why people throw the empty bottle to the recycle bin or even sort the waste before put it in the bin, it is probably because of social norm or attitude which can explain people behavior and action on recycling activity which can explain behavior of the respondents and their action on the activities regarding recycling. Attitude can be explained what are reasons behind their action or behavior. So we can understand the reason of Thai students’ reaction on recycling system and there is possibility to change attitude upon the time. From the above theory, we used to analyze weather after Thai student move to study in Sweden, have they change their attitude toward recycling system and participate in the container deposit system.
Attitude on Recycle and
container deposit system
Reasoned of ActionAttitude
Criteria for Acceptance
Diffusion of Innovation
17
On the other side, Diffusion of Innovation, expound the process of people to perceive the innovation since the recycling and container deposit system is a new issue for Thailand and not familiar with Thai people. So this model is important to demonstrate how the innovation system can infiltrate and might change the customer behavior.
The Last but not least, the model that authors choose to describe to the problem statement is the criterion for acceptance of innovation, this concept shows what are factors that people consider to accept the innovation.
18
4. Findings
4.1
Secondary FindingsThis chapter provides the secondary findings which will help to support the analysis part. First of all, we show the benefits of recycling. Then, we come up with the overview about recycling system, the bottles and cans production and the waste management in Thailand. Lastly, the information about container deposit system in European countries including their recycling system.
4.1.1 Benefits of Recycling
According to Pace butler Corporation, there are benefits of recycling. These benefits are good reasons why people should recycle. Firstly, financial income, people can turn things that are no longer use to money, for example, mobile phone or mobile battery can be purchased up to USD100 (pacebutler.com). Secondly, reduce consumption of resources or energy. It is the fact that to produce a new 1 aluminum requires using 6 ounce of gasoline or the equivalent of the energy to run a TV for three hours (recycling-revolution.com). So its production indeed consumes the resource which is nowadays in short supply. At this point, in 2007, United States of America recycled aluminum cans which can conserve the energy to more than 15 million barrels of oil which means very large amount number. In addition, the good recycling system will enhance the nation and global environment in terms of lowering the litters in the community (pacebutler.com).
4.1.2 Recycling system and container deposit system in Thailand
In the past, Thailand used to have a deposit system on soft drink glass. However, it was only an agreement between the beverage distributor and the retailers. The retailers had to pay some amount of money for the deposit to distributor whenever the bottles were delivered to them. The deposit will be returned when the bottles were sent back to distributors. The process is similar to container deposit system which is widely used in several countries at present. Somehow, the deposit system, which is run by government or company as Returpak in Sweden (National Renewable Energy Laboratory), has not yet implemented (Library.uru).
19
Now a day, the most popular method is that the recycling manufacturer buys the used aluminum from the person who collects. In terms of government, they encourage people to sort the waste and thrown into the blue recycle bin (Library.uru). In spite of having recycle bin provided, Thai people do not sort the waste before thrown it in the bin. Even if they do, it means nothing because all the solid waste was kept together in the same place at the end anyway (sawachin). According to the survey “why Thai people do not sort the waste”, the reason is mainly because habit of Thai people and the weakness of the structure (google survey, Why Thai people do not sort the waste?).
From time to time, the solid waste in Thailand has been continuously increased and it becomes a major problem especially in Bangkok, the capital city (DEDE). As mentioned in the beginning of the paper, most of the solid waste in Thailand was managed in the wrong method. There is approximately 16-34 percent of the total solid waste in Thailand that has a potential to be recycled, however, only 7 percent are actually recycled (Pollution control Department).
In terms of aluminum can, 350,000 units were produced in every 1 minute (Thai Restriction of Hazardous Substances. The advantage of Aluminum is that it can be reused at any unlimited times. Conversely, it effects to the environment.
Nowadays government tries to launch the recycling campaign in the hope that they can encourage people to put more concern and turn into action. However, the bill concerning the recycling has not issued yet in Thailand. Anyhow, according to the Department of the Environmental Quality Promotion, there are several methods of refuse disposal, for example, incineration, composting method and landfill (tungsong.com).
In terms of environmental program, we found that high cost of implementing an environmental program is the chief barrier to the adoption of green purchasing and environmental sound practice (Min and Galle, 1997). In fact, there is internal driving, for instance, the top management in the organization (James et al., 1999), and external driving including governments, and local communities in order to push the environmental practices to become real and practical (Henriques and Sadorsky, 1996).
20
4.1.3 Container deposit system in European countries
Now a day, there are many states in US, it is work well in New York to boost up recycle rate and several countries in Europe such as Denmark, Sweden and Germany and also South Australia that consider the little and waste from aluminum can and plastic bottle are the serious problem to the environment and it cost to the country to tackle these waste. The container deposit system was implemented to handle this problem and expected to reduce number of waste. In Germany the term “Pfand” is used which means deposit, while in Sweden used “Pant” which mean mortgage. And some country in Europe interest in this system to manage their as waste as well such as in UK that they face a problem of rubbish on the street which have more than 500 percent growth since 1960s and they need to spend £500 million per year to manage them. In UK, They are 80% of public to support this system and assure in the system (John and Louise,2009) ( Guardian, 2009)
Furthermore, there have an agreement among European country in term of material recycling. In Sweden which implement container deposit system also have a rising rate in recycle rate. In 2006, the recycling rate increase to 81 percent comparing to year 2005 which recycling rate was 56 percent. This performance met to the EU’s target goal for each country to participate in environment sustainability. As show in Figure 4 by Swedish EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) reported for year 2008. About container deposit system in Sweden that implement on plastic bottle (PET) and aluminum can achieve 86 percent in 2006 and this number illustrate the success of this system which people return the container on provided station (Swedish Waste Management, n.d.)
21
Figure 4: 2006 & 2005 results of packaging collection
Source: (Naturvårdsverket, 2008)
In Germany, the failure of container deposit was present to manufacture in order to consumer refuse to buy a can product and consume bottle product instead. Germany is the one of European country who had a complicate container deposit system as customer have to return the used package back to the same store to get deposit back. And also the deposit rate of the aluminum can product is higher comparing to glass bottle which are 25 Euro cent for aluminum can and 8 euro cent for glass bottle. (Return Container,2008) This system did not get a well participate from people and the average achieve only 40 percent. The significant change when Germany was force by European regulators to change the container deposit to integrity (Food production daily, 2004). People can return used can to any store and increase automatic receive station, the new deposit system can increase the collection rate and can achieve to 95 percent (R3 consulting group, 2009)
In figure 5 below show the achievement of container deposit system from selected place that implement the system such as in the state, Canada, Germany, Finland and Sweden. Moreover it illustrate the amount of deposit in each country as well
22
Figure 5: Recycle rate and amount of deposit
23
4.2
Primary FindingsAfter distributing the questionnaire to Thai students who are studying in Sweden, we have got 107 respondents. According to the sampling qualification mentioned above, we will sort out 7 respondents who have been living in Sweden more than 2 years. Therefore, 100 respondents totally will be used as the valid data for analyzing.
4.2.1 Questionnaire Part1: Demographic (Questions 1-3)
This part provides the demographic data. It consists of gender, age and latest education level.
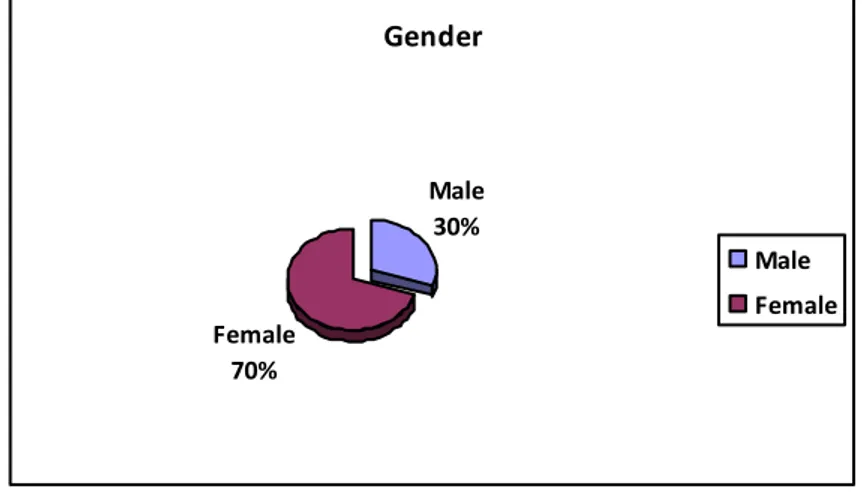
Gender Male 30% Female 70% Male Female Figure 6: Gender
30% of the respondents are male and 70% of the respondents are female.
Age 12% 69% 14% 5% 18-23 years old 24-27 years old 28-30 years old
more than 30 years old
24
12% of the respondents are varied between 18 and 23, 69% of the respondents are between 24 and 27, 14% are between 28 and 30 and 5% are above 30 years old.
Latest education level
39% 59% 2% Bachelor's Degree Master's Degree Doctural's Degree
Figure 8: Lastest education level
39% of the respondents are Bachelor’s, 59% are Master’s and 2% are Ph.D.
4.2.2 Questionnaire Part2 (A): Knowledge (Questions 5-8 and 24-27)
Questionnaire part 2 compares the knowledge of Thai students in Sweden about recycling and container deposit system before came to Sweden and after come to Sweden. The finding from this part can be used to measure and interpret in terms of diffusion of innovation.
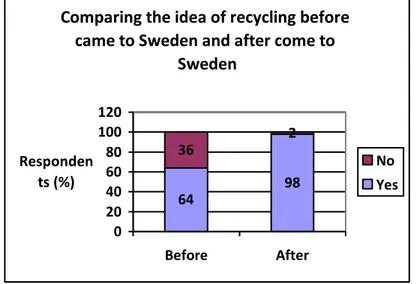
Comparing the idea of recycling before came to Sweden and after come to
Sweden 64 98 36 2 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 Before After Responden ts (%) No Yes
Figure 9: The idea about recycling and container deposit system
Figure 9 shows that before the respondents came to Sweden, 64% of them had thought about the recycling. 36% had never thought about it. After they come to Sweden, the idea was changed. The numbers of respondent who have thought about the recycling increased to 98%.
25
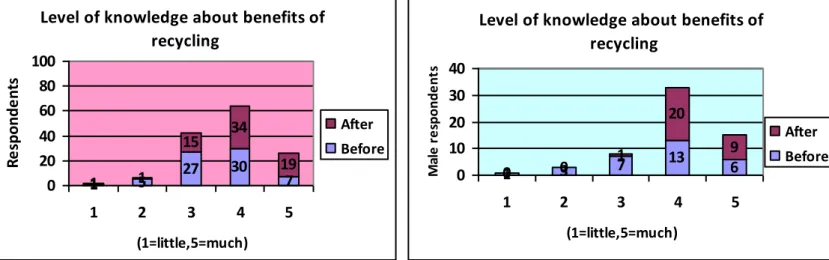
Figure 10 Comparison level of knowledge about recycling between female and male
Figure 10 above shows that majority of the respondents both female and male had neutral knowledge about recycling before came to Sweden. After they come to Sweden, most of the respondents increased their level of knowledge.
Figure 11: Comparing level of knowledge about benefits of recycling between male and female
Figure 11 above shows that majority of the respondents both male and female had more slightly knowledge about benefits of recycling before they came to Sweden. After they come to Sweden most of them increased their knowledge.
Level of knowledge about recycling
3 4 13 9 1 0 0 3 17 10 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 1 2 3 4 5 (1=little,5=much) M al e r e sp o n d e n ts After Before
Level of knowledge about recycling
1 10 35 21 3 1 0 9 47 13 0 20 40 60 80 1 2 3 4 5 (1=little,5=much) Fe m al e r e sp o n d e n ts After Before
Level of knowledge about benefits of recycling 1 3 7 13 6 0 0 1 20 9 0 10 20 30 40 1 2 3 4 5 (1=little,5=much) M al e r e spond e nt s After Before Level of knowledge about benefits of
recycling 1 5 27 30 7 1 1 15 34 19 0 20 40 60 80 100 1 2 3 4 5 (1=little,5=much) Fe m al e R e sp o n d e n ts After Before
26
*Remark: CDS refers to Container Deposit system
Figure 12: Comparison level of knowledge about Container deposit system (CDS) between female and male
According to figure 12, most of the respondents both female and male had little knowledge about container deposit system before they came to Sweden. They increased level of knowledge after they come to Sweden.
Level of knowledge about CDS
17 21 21 8 3 0 0 3 29 38 0 10 20 30 40 50 1 2 3 4 5 (1=little,5=much) Fe m al e R es p o n d en ts After Before
Level of knowledge about CDS
7 9 7 4 3 0 0 3 12 15 0 5 10 15 20 1 2 3 4 5 (1=little,5=much) M al e r e spond e nt s After Before
27
4.2.3 Questionnaire Part2 (B): Attitude (From choice 9-21 and 28-40)
This part shows the attitudes toward recycling and container deposit system before came to Sweden and after they come to Sweden. 6 points Likert scale has been used in the survey questionnaire in order to measure the attitude. 6 rating scale refers as following;
1= strongly disagree 4= partly agree
2= disagree 5= agree
3= partly disagree 6= strongly agree
1= Strongly disagree 6= Strongly agree
Before After
1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6
1.Recycling is important 2 7 13 23 26 29 1 0 5 13 37 44
2.I don’t mind about the recycling 29 24 18 14 9 6 53 28 6 5 4 4
3.Container deposit system will help reduce the waste
3 12 21 22 18 24 1 2 4 11 30 52
4.It is wasting my time to return the container at the machine
19 23 14 18 21 5 35 34 13 7 6 5
5.Container deposit system is an efficient way to recycling
2 9 27 27 23 12 1 0 7 11 32 49
6.I am willing to pay extra money for deposit
14 25 24 18 13 5 2 8 14 18 26 32
7.I think I will sort the waste in the recycle bin provided
14 26 25 16 16 3 2 2 11 21 31 33
8.I think I will sort the waste even though there is no recycle bin around me
24 34 17 15 7 3 2 6 24 24 30 14
9.I think deposit system effects my buying decision
11 27 14 23 10 5 17 11 18 27 19 8
10.It’s inconvenience to return the bottle at the machine
10 20 24 24 15 7 26 36 16 10 7 5
11.I think I would convince my friends/family to use the deposit system
11 26 25 21 12 5 2 1 10 26 29 32
12.I think deposit system is complicated system
10 31 26 15 13 5 35 38 13 6 7 1
13.I think container deposit system can reduce the energy to produce the new one
3 9 25 23 19 21 1 5 6 8 31 49
28
The table above shows the comparison of the attitude toward recycling and container deposit system before came to Sweden and after they come to Sweden. The number in the table represents the quantity of respondents. The red one is the highest rank that respondents choose. Mostly, we can see that number of respondents increased in the positive way. For example, recycle is important (question 1), most of respondents strongly agree with this statement (29%) before they came to Sweden. However, after they come to Sweden, their attitude toward recycling has changed. The number of respondents who strongly agree with this statement increased to 44% which means that more people give more important to the recycling after they come to Sweden.
Another example is statement number 4, according to the table above shows that the attitude of the respondents has changed. Before they came to Sweden, 23% of the respondents had thought that it was quite wasting their time to return the container at the redemption center. However, after they come to Sweden, most of them (35%) did not think that container deposit system would waste their time.
According to figure 13 which presents the attitude of the respondents, we can divide into 2 groups based on the gender. The following graph shows the relationship between gender and attitude.
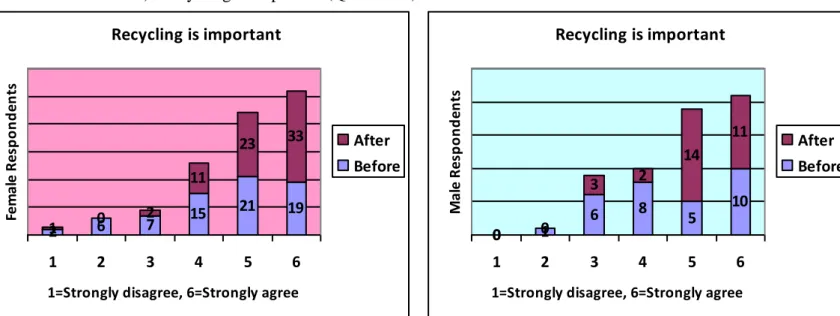
a.) Recycling is important (Question 9)
Figure 14: Comparison the importance of recycling between female and male
Most of female respondents agreed that recycling is important before they came to Sweden while majority of male strongly agreed. However, after they come to Sweden, most of female
Recycling is important 2 6 7 15 21 19 1 0 2 11 23 33 1 2 3 4 5 6
1=Strongly disagree, 6=Strongly agree
Fem al e R es p o n d en ts After Before Recycling is important 0 1 6 8 5 10 0 0 3 2 14 11 1 2 3 4 5 6
1=Strongly disagree, 6=Strongly agree
M al e R es p o n d en ts After Before
29
I do not mind about recycling
9 6 3 8 3 1 13 9 3 1 2 2 1 2 3 4 5 6
1=Strongly disagree, 6=Strongly agree
M al e R es p o n d en ts After Before I do not mind about recycling
20 18 15 6 6 5 40 19 3 4 1 3 1 2 3 4 5 6
1=Strongly disagree, 6=Strongly agree
Fem al e R es p o n d en ts After Before
respondents have shifted to strongly agree. Conversely, majority of male agreed with the statement.
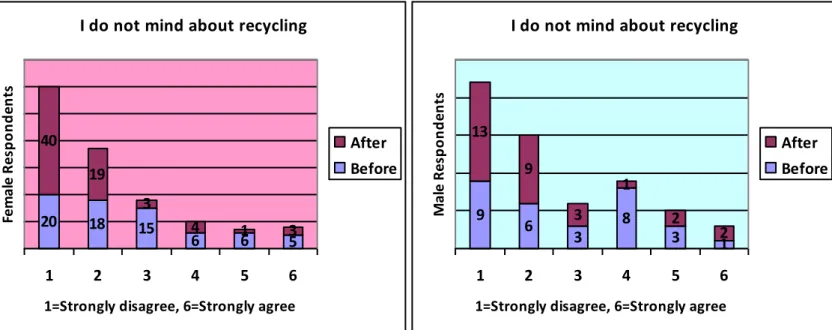
b.) I don’t mind about recycling. (Question 10)
Figure 15: Comparison concerning of recycling between female and male
Most of the female respondents strongly disagreed with the statement before came to Sweden which is similar to male. However, it is clearly seen that after they come to Sweden, the number of both groups who strongly disagreed with this statement increased
c.) Container deposit system (CDS) will help reduce the waste. (Question 11)
Figure 16: Comparison the attitude that CDS can reduce the waste between female and male CDS will help reduce the waste
1 10 14 13 17 15 1 1 3 7 21 37 1 2 3 4 5 6
1=Strongly disagree, 6=Strongly agree
Fem al e R es p o n d en ts After Before
CDS will help reduce the waste
2 2 7 9 1 9 0 1 1 4 9 15 1 2 3 4 5 6
1=Strongly disagree, 6=Strongly agree
M al e R es p o n d en ts After Before
30
CDS is an efficient way to recycling
0 6 21 15 18 10 1 0 4 6 23 36 1 2 3 4 5 6
1=Strongly disagree, 6=Strongly agree
Fem al e R es p o n d en ts After Before
CDS is an efficient way to recycling
2 3 6 12 5 2 0 0 3 5 9 13 1 2 3 4 5 6
1=Strongly disagree, 6=Strongly agree
M al e R es p o n d en ts After Before
Majority of the female respondents agreed that CDS will help reduce the waste while the number of male who partly agree and strongly agree is the same before they came to Sweden. However, after they come to Sweden, majority of female switched to strongly agree which is similar to male.
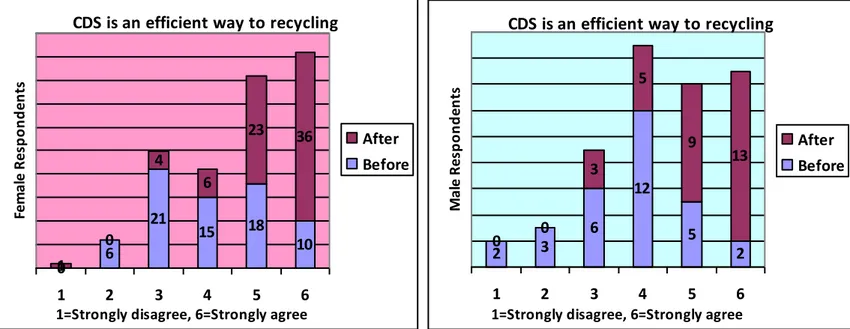
d.) Container deposit system (CDS) is an efficient way to recycling. (Question 13)
Figure 17: the attitude that CDS can reduce the waste between female and male
Above charts show the attitude between male and female about efficiency of CDS. For female, before they came to Sweden, most of them are agree with container deposit system even 21 of respondents are partly disagree. But after they come to Sweden, female respondents have better attitude about efficiency of CDS by there are 36 respondents strongly agree with this system. Same as male respondents, they have better attitude to this system and they result show the attitude move from partly agree to strongly agree.
31
e.) I think I will sort the waste in the recycle bin provided. (Question 15)
Figure 18: Comparison behavior of sorting waste between female and male
The majority of female partly disagreed with the statement which means that before they came to Sweden, they did not think that they would sort the waste in the recycle bin provided. However, after they come to Sweden, their attitude has changed. Most of them strongly agree with this statement. It can be explained that after they come to Sweden, they think they will sort the waste in the recycle bin which is similar to male.
f.) I will sort the waste even though there is no recycle bin around me. (Question 16)
Figure 19: Comparison behavior of sorting waste even no recycle around there I will sort the waste in the recycle bin
provided 15 20 19 8 10 1 2 2 7 15 22 22 1 2 3 4 5 6
1=Strongly disagree, 6=Strongly agree
Fem al e R es p o n d en ts After Before
I will sort the waste in the recycle bin provided 2 6 6 8 6 2 0 0 4 6 9 11 1 2 3 4 5 6
1=Strongly disagree, 6=Strongly agree
M al e R es p o n d en ts After Before
I will sort the waste even though there is no recycle bin around me
18 26 13 6 5 2 2 5 18 16 20 9 1 2 3 4 5 6
1=Strongly disagree, 6=Strongly agree
Fem al e R es p o n d en ts After Before
I will sort the waste even though there is no recycle bin around me
2 3 6 12 5 2 0 0 3 5 9 13 1 2 3 4 5 6
1=Strongly disagree, 6=Strongly agree
M al e R es p o n d en ts After Before
32
Before came to Sweden, majority of female (26%) did not think that they would sort the waste even though there is no recycle bin around them. After they come to Sweden, their attitude altered, most of them agree with statement. It means that they think that they will sort the waste. On the other hand, most of male respondents partly agreed with the statement before come to Sweden. The number of male respondents has switched to strongly agree when they come to Sweden.
g.) I think container deposit system can reduce the energy to produce the new one. (Question 21)
Figure 20: Comparison attitude that CDS can reduce energy
Before came to Sweden, most of the female did not think that the container deposit system could reduce the energy to product the new one comparing to male, most of them partly agreed with this statement. After come to Sweden, most of the female strongly agree which is similar to male. According to figure 20, this means that after people come to Sweden, their attitude has changed as well as their increased knowledge in terms of recycling.
CDS can reduce the energy to produce the new one 2 6 23 11 13 15 1 3 3 1 25 37 1 2 3 4 5 6
1=Strongly disagree, 6=Strongly agree
Fem al e R es p o n d en ts After Before
CDS can reduce the energy to produce the new one 1 3 2 12 6 6 0 2 3 7 6 12 1 2 3 4 5 6
1=Strongly disagree, 6=Strongly agree
M al e R es p o n d en ts After Before
33
4.2.4 Questionnaire Part2 (C): Behavior (From choice 22-23 and 41-42)
This part provides the data concerning respondents’ behavior. It consists of purchasing frequency (can and PET) and numbers of can and PET that they thrown into the recycle bin comparing before came to Sweden and after they come to Sweden.
0 20 40 60 80 R e sp o n d e n ts ( % ) Before After
How much do you buy aluminum can and PET
Less than 7 bolttles/week 8-14 bottles/week 15-21 bottles/week more than 21 bottles/week
Figure 21: Can and PET purchasing frequency
The majority of respondents (61%) bought can and PET less than 7 bottles per week before came to Sweden. After they come to Sweden, buying less than 7 bottles per week is the top frequency for respondents (68%).
91513 22 41 47 24 10712 0 10 20 30 40 50 R e sp o n d e n ts ( % ) Before After
How much do you think you thrown the Can and PET in the recycle bin
100-80% 79-60% 59-40% 39-20% 19-0%
Figure 22: number of respondents who thrown can and PET into the recycle bin.
Before the respondents came to Sweden, majority of them (41%) had thrown just 0-19% of the can and PET into the recycle bin. Conversely, when they come to Sweden, almost 100% of the can and PET are thrown into the recycle bin.
34
Purchasing frequency and percentage of recycle BEFORE came to Sweden 3 5 1 0 10 4 0 1 6 5 1 1 16 5 0 1 26 13 1 1 Less than 7 units
8-14 units 15-21 units more than 21 units How many bottle customer buy per week
Re sp o n d en ts 19-0% 39-20% 59-40% 79-60% 100-80%
Figure 23: Purchasing Frequency and percentage of recycle BEFORE came to Sweden.
Figure 23 shows the behavior BEFORE respondent came to Sweden. This graph illustrates how much respondent buy aluminum can and PET bottle each week and how many percent that they throw in the recycle bin. Majority respondent ( 61 persons) buy aluminum can and PET bottle less than 7 units per week and 26 out of 61 persons was throw to recycle bin only 19-0%. And also for people who buy aluminum can and PET between 8-14 units per week 13 persons out of 32 persons have only 19-0% to throw the empty container to the recycle bin. This statistic indicated since respondents live in Thailand, it is a low chance that they thrown the empty container in the recycle bin. And some of them never throw it to recycle bin as well. Inspire of there are some people which is minority who always (100-40%) thrown them to recycle bin. From this information can infer that there will be a lot of empty container was not put in the right place.
35
Purchasing frequency and percentage of recycle AFTER come to
Sweden
34 10 1 2 14 7 2 1 5 4 1 0 5 2 0 0 10 1 1 0Less than 7 units 8-14 units 15-21 units more than 21 units
How many bottle customer buy per week
R espo nd ent s 19-0% 39-20% 59-40% 79-60% 100-80%
Figure 24: Purchasing Frequency and percentage of recycle AFTER come to Sweden.
From figure 24 show the behavior AFTER respondents came to Sweden. This graph illustrate how much respondent buy aluminum can and PET bottle each and how many percent that they throw in the recycle bin. There are 68 persons who buy aluminum can and PET less than 7 units. 24 persons who buy aluminum can and PET between 8 – 14 units per week. 5 persons who buy aluminum can and PET 15-21 units per week and 3 persons who buy aluminum can and PET more than 21 units per week.
Majority respondent (68 persons) buy aluminum can and PET bottle less than 7 units per week and 34 out of 68 which is 50% of these people have 80-100% throw the empty container in the recycle bin. And other respondents who often buy aluminum can and PET bottle 8-21 units and over mostly throw the empty container to the recycle bin. And from total respondents 100 persons, there are just only 12 persons who have low rate of return empty container to recycle bin.