School of Health and Welfare, Jonkoping University
Determination of thyroid volume
by ultrasound
NGUYEN THI THU
Thesis, Bachelor degree, 15 ECTS
Radiography
Jonkoping and Da Nang April 2016
Supervisors: Vo Ho Quynh Nhu Thomas Ehn Examiner: Berit Bjorkman
CONTENT
ABSTRACT
... 3
INTRODUCTION ... 4
BACKGROUND ... 5
Ultrasound ...5 Ultrasound machine ... 5Physical basis of ultrasound ... 6
Operating Principles ... 7
Thyroid ...7
Ultrasound of the thyroid. ... 10
Radiographer and radiography ... 10
AIM ... 11
MATERIAL AND METHOD ... 11
Data collection ... 12
Ultrasound machine be used in this study. ... 12
Thyroid ultrasound technique ... 13
Method ... 13
ETHICAL CONSIDERATION ... 14
RESULT ... 14
DISCUSSION
... 17
Our thoughts about the role of the radiographer: ... 18
CONCLUSION ... 19
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... 20
REFERENCES ... 20
ABSTRACT
Background: Ultrasound is safe and painless, produces pictures of the inside of the body
using sound waves (not use ionizing radiation), thus there is no radiation exposure to the patient. The thyroid gland is among the most commonly imaged glands using ultrasound due to the limitation of clinical examination.
The Radiographers' skills in ultrasound differ according to the country and the basic formations. And throught this study we want to emphasize about the role of radiographer.
Aim: The porpuse of this study is determine the volume and morphological characteristics of
normal thyroid order to get reference values for young adults.
Material and Method: We selected 204 students consist of male and female from Danang
University of Medical Technology And Pharmacy were studied. Mean age of our subjects was 22 (range 18-25) all of them were healthy and with normal thyroid gland status. Descriptive statistics and analytic statistic was used.
Results: In our study, the thyroid volume between female and male is different. The total
thyroid volume significantly correlated with individual’s height, weight, body surface area and body mass index. The mean of total thyroid volume was 7.44 ± 2.09ml (range 3.51-14.57). The thyroid volume was best correlated with height (r = 0.44; p = 0.0001).
Conclusion: Knowledge about the size of the thyroid gland is important in following the
thyroid diseases and the examination of the gland.
The radiographer's role is very important in determining the volume of thyroid. Radiographer is an important member of the diagnostic health care team.
INTRODUCTION
In a normal thyroid volume may vary in different countries, different geographic regions or nations [1]. It does not change just according to height, weight, gender or age but also vary by stage of development of individual physiology. Especially, it is very sensitive to the amount of iodine contained in everyday foods. According to WHO, the volume determination of thyroid gland with ultrasound for normal people in a residential area is regarded as a tool to assess the state of iodine deficiency in that community. Examinations with medical ultrasound is a painless procedure to examine the function and in some cases pathology of the internal organs of the body. It uses sound waves of high frequency to make images of the body [2]. Ultrasound has become one of the primary imaging modality for the assessment of the major glands of internal secretion within the cervical region. Ultrasound scanning is non-invasive, widely available, inexpensive, and does not use ionizing radiation [3]. The thyroid gland is among the most commonly imaged glands using ultrasound due to the limitation of clinical examination. Thyroid diseases are common in Vietnam: Goiter (thyroid bulge alone), grave disease (basedow), thyroid nodules, thyroiditis. According to a study in Dong Thap preventive medicine centers: Total patients examined at the central clinic (2006) were 5061 cases. Including 4363 cases goiter of many kinds, percentage: 86.20% [4].
Evaluation of the thyroid volume could be performed using several imaging techniques. These modalities include plain radiography, radionuclide imaging, ultrasonography, Computed Tomography (CT), and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Each technique has it’s advantages and limitations, such as CT and MRI provide structural information of the thyroid gland just like ultrasound, but they are relatively more expensive and use radiation (CT) [5,6]. Therefore, one of the purposes of this study was to point out the benefits of ultrasound when used in the determination of thyroid volume and morphology to assess status the thyroid gland and helps early discovery of thyroid abnormalities such as: cysts, nodules and tumors [7]. In Vietnam, ultrasound was performed by radiologist. Radiographers are often trained in several specialist areas such as: Trauma radiography - challenging examinations on injured individuals. Mobile radiography - for patients too sick to travel to the X-ray department. Computed tomography - three dimensional X-ray imaging test. Magnetic resonance imaging - three dimensional imaging test powered by a large magnet. Fluoroscopy – X-ray test that examines the internal body and shows moving images on a screen like a movie. Angiography - imaging of blood vessels and the heart. Operating theatre - assisting surgeons during
and effects of disease when taking X-ray images. So, we hope in the future radiographers maybe allowed to perform an ultrasound technique. To be able to better support radiologists and doctors to diagnose or monitor a patient's injury or illness.
BACKGROUND
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging is also called ultrasound scanning, involves the use of a small transducer (probe) and ultrasound gel placed directly on the skin. High-frequency sound waves are transmitted from the probe through the gel into the body. The transducer collects the sounds that bounce back and a computer then uses those sound waves to create an image [7]. Ultrasound examinations do not use ionizing radiation (as in x-ray), thus there is no radiation exposure to the patient. Because ultrasound images are captured in real-time, they could show the structure and movement of the body's internal organs, as well as blood flowing through blood vessels. Ultrasound imaging is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions [8].
The Radiographers' skills, in ultrasound, differ according to the country and the basic formations. In Viet Nam, ultrasound is a diagnostic exam performed by medical doctors or sonographer (a person who performs diagnostic ultrasound procedures).
We hope in the future radiographers maybe allowed to perform an ultrasound technique if they fulfill the number of hours in the theoretical and practical lessons in ultrasound. This do require further training and the completion of a graduate diploma.
Ultrasound machine
Ultrasound scanners consist of a console containing a computer and electronics, a video display screen and a transducer that is used to do the scanning. The transducer is a small hand-held device that resembles a microphone, attached to the scanner by a cord. The transducer sends out inaudible high frequency sound waves into the body and then listens for the returning echoes from the tissues in the body [9]. The principles are similar to sonar used by boats and submarines.
The ultrasound image is immediately visible on a video display screen that looks like a computer or television monitor. The image is created based on the amplitude (loudness), frequency (pitch) and time it takes for the ultrasound signal to return from the area of the patient being examined to the transducer (the device used to examine the patient), as well as
the type of body structure and composition of body tissue through which the sound travels. A small amount of gel is put on the skin to allow the sound waves to travel back and forth from the transducer [9].
Physical basis of ultrasound
Sound waves are created by converting electrical energy into shock wave similar to the X-ray emission, emitted from the probe, the basic structure is the piezoelectric ceramic or crystal. Sound waves are only transmitted through the material without passing through the vacuum, because there is no vibration [10].
One of the most basic characteristics is the frequency of sound waves depends on the nature of the objects and have different vibration. The measuring unit is the hertz frequency, is the number of oscillation cycles per second [10].
The nature of ultrasound: To understand ultrasound you have to understand that it is the sine wave oscillator frequency from 20Hz - 20,000Hz. If low-frequency sound waves <20Hz called Lower sound; >20,000Hz called ultrasound. Medical ultrasound use sound waves with frequencies from 2 MHz to 20 MHz [11].
Characterization of Ultrasound: The spread of sound waves - Attenuation and absorption: In environments with heterogeneous structures, acoustic wave propagation in a straight line, and gradually lose energy is called attenuation. Acoustic wave velocity depends on the hardness and density of the physical environment through, in the human body: fat in 1,450 m/s; water in 1,480 m/s; Soft tissue in 1,540 m/s; Bone in 4,100 m/s [11].
The reflex or response: In environments with heterogeneous structures, a sound wave section will respond in a plane perpendicular to the beam of sound waves create echoes and reverbs (echo), the rest will be spread in the direction of the sound beam discovered out. Thus, at the boundary between 2 media with negative impedance (acoustic impedance), denoted Z, Z varies depending of the physical structure of atoms in the particular tissue. Wave feedback collected by the probe will then be processed in the machine and transmit images onto the screen (display), or recorded on film, printing paper or on tape from the disk [11]. The feedback waves were detected by the probe will disappear under the laws of decline.
Refraction, noise: As the beam passes through the plane of separator with a small angle, the beam emitted sound will be regressed some negative compared to a beam known as crosstalk [11].
Operating Principles
Ultrasound is based on the same principles of operation as the navigation system in boats and bats. When a sound wave strikes an object, it bounces back, or echoes. By measuring these echo waves it is possible to determine the distance as well as the size, shape and density (taking into solid objects, or fluid-filled, or both) of the object [11].
An ultrasound transducer both sends the sound waves and records the echoing waves. When the probe is pressed against the skin, it directs small pulses of high frequency sound waves transducer enters the body. As the sound waves bounce off the organs, fluids and tissues inside the body, a very sensitive microphone in the transducer records tiny changes in the elevation and direction of the sound [11]. The signals will be measured immediately and shown by a computer by creating images in real time on the screen. There are one or more frames to be captured as a still image.
Doppler ultrasound is a special application of ultrasound, are used to measure the direction and speed of blood cells as they circulate in the bloodstream. The movement of blood cells causes a change in pitch of the reflected sound waves called the Doppler‘s effect. A computer collects and processes the sounds and creates graphs or color pictures that represent the flow of blood in the blood vessels [11].
Thyroid
The thyroid is a gland at the front of the neck, below the larynx (commonly called the voice box). The thyroid has 2 lobes, one on each side of the trachea (windpipe). The 2 lobes are connected by a thin bridge of thyroid tissue called the isthmus (picture 1) [12].
Picture 1: Antomy of the thyroid and parathyroid glands.[13]
Inside, the gland is made up of many hollow follicles, whose epithelial cell walls (also known as follicle cells) surround a central cavity filled with a sticky, gelatinous material called colloid. Parafollicular cells are found in the follicle walls, protruding out into the surrounding connective tissue.The thyroid is the largest exclusively endocrine gland in the body. The endocrine system is the body’s communication hub, controlling cell, and therefore organ, function. A primary goal of the endocrine system is to maintain homeostasis within the organism, despite external fluctuations of any sort. Hormones, which act as chemical messengers, are the mechanism for this communication. The hormones secreted by the thyroid gland are essential in this process, targeting almost every cell in the body (only the adult brain, spleen, testes, and uterus are immune to their effects). Inside cells, thyroid hormone stimulates enzymes involved with glucose oxidation, thereby controlling cellular temperature and metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Through these actions, the thyroid regulates the body’s metabolic rate and heat production. Thyroid hormone also raises the number of adrenergic receptors in blood vessels, thus playing a major role in the regulation of blood pressure. In addition, it promotes tissue growth, and is particularly vital in skeletal, nervous system, and reproductive development [12].
The normal thyroid gland [Figure 1] consists of 2 lobes and a bridging isthmus. Thyroid size, shape and volume varies with age and sex. Normal thyroid lobe dimensions are: 18-20 mm longitudinal and 8-9 mm antero-posterior (AP) diameter in newborn; 25 mm longitudinal and 12-15 mm AP diameter at one year age; and 40-60 mm longitudinal and 13-18 mm AP
diameter in an adult population. The limits of normal thyroid volume (excluding isthmus, unless its thickness is >3 mm) are 10-15 ml for women and 12-18 ml for men [14].
Figure1: the normal thyroid gland (Gray scale ultrasound, transverse scan)[15]
Diseases and Disorders of the Thyroid
Knowledge about the size of the thyroid gland is important in following the thyroid diseases and the examination of the gland. There are many diseases and disorders associated with the thyroid. They can develop at any age and can result from a variety of causes - injury, disease, or dietary deficiency, for instance. But in most cases, they can be traced to the following problems: Too much or too little thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, respectively) abnormal thyroid growth nodules or lumps within the thyroid, thyroid cancer. Below are some of the most common thyroid disorders [16]
Goiters: A goiter is a bulge in the neck. A toxic goiter is associated with hyperthyroidism, and a non-toxic goiter, also known as a simple or endemic goiter, is caused by iodine deficiency [15].
Hyperthyroidism: Hyperthyroidism is caused by too much thyroid hormone. People with hyperthyroidism are often sensitive to heat, hyperactive, and eat excessively. Goiter is sometimes a side effect of hyperthyroidism. This is due to an over-stimulated thyroid and inflamed tissues, respectively [16].
Hypothyroidism: Hypothyroidism is a common condition characterized by too little thyroid hormone. In infants, the condition is known as cretinism. Cretinism has very serious side effects, including abnormal bone formation and mental retardation. If you have hypothyroidism as an adult, you may experience sensitivity to cold, little appetite, and an
overall sluggishness. Hypothyroidism often goes unnoticed, sometimes for years, before being diagnosed [16].
Solitary thyroid nodules: Solitary nodules, or lumps, in the thyroid are actually quite common—in fact, it’s estimated that more than half the population will have a nodule in their thyroid. The great majority of nodules are benign. Usually a fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNA) will determine if the nodule is cancerous [16].
Thyroid cancer: Thyroid cancer is fairly common, though the long-term survival rates are excellent. Occasionally, symptoms such as hoarseness, neck pain, and enlarged lymph nodes occur in people with thyroid cancer. Thyroid cancer can affect anyone at any age, though women and people over thirty are most likely to develop the condition [16].
Thyroiditis: Thyroiditis is an inflammation of the thyroid that may be associated with abnormal thyroid function (particularly hyperthyroidism). Inflammation can cause the thyroid’s cells to die, making the thyroid unable to produce enough hormones to maintain the body's normal metabolism [16].
Ultrasound of the thyroid.
Thyroid ultrasound uses sound waves to produce pictures of the thyroid gland within the neck. It does not use ionizing radiation and is commonly used to evaluate lumps or nodules found during a routine physical or other imaging exam [17].
An ultrasound of the thyroid produces pictures of the thyroid gland and the adjacent structures in the neck [17].
This procedure requires little to no special preparation. Leave jewelry at home and wear loose, comfortable clothing [17].
Ultrasound is very sensitive and shows many nodules that cannot be felt. In some age groups, nodules are seen on ultrasound in as many as 70 % of adults. The vast majority of these are benign regions of thyroid tissue that pose no health risk. The minority of these are true tumors of the thyroid and may require further diagnosis or treatment [7].
Radiographer and radiography
A radiographer is a trained health professional who performs medical imaging by producing high quality X-ray pictures or images used to diagnose and treat injury or disease. A radiographer is an important member of the diagnostic health care team. Their roles are diverse and challenging [in Inside Radiography-The Radiographer (Medical Imaging
The radiographer works in a highly advanced technical profession, they work in a variety of situations including radiography/medical imaging departments of large public hospitals with busy emergency departments, private hospitals and large and small private radiology practices, sometimes with only a couple of rooms and a few staff. That also requires excellent people skills [in Inside Radiography-The Radiographer (Medical Imaging Technologist)]. Radiography is radiographer’s main field, the professional field of knowledge, research and hence also of responsibility.
RATIONALE
Ultrasound has become one of the primary imaging modality for the assessment of the major glands of internal secretion within the cervical region. Ultrasound scanning is non-invasive, widely available, inexpensive, and does not use ionizing radiation [3].
The thyroid gland is among the most commonly imaged glands using ultrasound due to the limitation of clinical examination.
Knowledge about the size of the thyroid gland is important in following the thyroid diseases and the examination of the gland. There are many diseases and disorders associated with the thyroid. They can develop at any age and can result from a variety of causes - injury, disease, or dietary deficiency, for instance. But in most cases, they can be traced to the following problems: Too much or too little thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, respectively) abnormal thyroid growth nodules or lumps within the thyroid, thyroid cancer. I'm a technician. I'd been conducting research on measuring the size of adult thyroid normal to have a certain amount of knowledge about ultrasound, thyroid and how the measurement data gathering research. As well as better understand how to do research. Making reference parameter is the size of normal human thyroid aged 18-25. Consent and enthusiastic help from the instructors, medical imaging department of Da Nang University of Medical Technology and Pharmacy, the medical diagnostic center Danang, I conducted a study titled: Determination of thyroid volume by ultrasound.
AIM
The aim of study was to determine the volume and morphological characteristics of normal thyroid in order to get reference values for young adults age 18-25.
MATERIAL AND METHOD
This study was an experimental study using a quantitative method to determine the thyroid volume of young adults.
Data collection
We randomly selected 210 students in Danang University Of Medical Technology And Pharmacy consist of male and female were studied. (When we come to school for collect the data of research. The school organized general health check for freshman. Therefore, we can get data easily.) The age of the subjects ranged from 18-25 years.
The examination is done by Dr.Vo Ho Quynh Nhu with ultrasound machine, fitted with a 7.5MHz transducer (linear array probe with high frequency, 5-13MHz). Examination table, ultrasound gel, examination glove and paper or tower.
Subjects with anterior neck swelling or clinical evidence of thyroid disease were excluded from the study. Also excluded from the study were women during menstruation, pregnant women or women who have delivered within the last 12 months.
Ultrasound machine be used in this study.
In this study we used an ultrasound machine at the Medical Imaging Department at Da Nang. University of Medical Technology and Pharmacy, Da Nang, Vietnam. Hitachi Aloka model: F37, made in Japan (Figure 2).
Figure 2: This is the ultrasound machine used in study [photo by Dr.Vo Ho Quynh Nhu]. Hitachi Aloka model: F37, made in Japan
Thyroid ultrasound technique
Requirements for participants: Subjects should wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing for subjects ultrasound exam. Subjects could need to remove all clothing and jewelry in the area to be examined. Subjects could be asked to wear a gown during the procedure.
Subjects will be positioned lying face-up on an examination table that could be tilted or moved. A pillow may be placed behind the shoulders to extend the area to be scanned for a thyroid ultrasound exam [7].
After subjects are positioned on the examination table, the sonographer will apply a warm water-based gel to the area of the body being studied. The gel will help the transducer make secure contact with the body and eliminate air pockets between the transducer and the skin that could block the sound waves from passing into the subject body. The transducer is placed on the body and moved back and forth over the area of interest until the desired images are captured [11].
The width and depth are measured on transverse section of the lobe: the width is the distance between the most lateral point of the lobe and the acoustic shadowing of the trachea and the depth is the maximum anterior-posterior distance in the middle third of the lobe. The length is measured on longitudinal section and it is the maximum distance from the most cranial to the most caudal part of the lobe [18].
Method
Descriptive statistics and analytic statistic was used. The data were collected and analyzed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) for windows version 16 and a p<0.05 was taken as significant. The statistician from Da Nang university of Medical Technology and Pharmacy help us to process the data collected on SPSS.
Laboratory values were reported as mean ± SD, percentage, maximum, minimum and interquartile range.
The thyroid gland volume was calculated using the formula below: Volume = length x width x thickness x 0.479 (conversion factor)[11] In that: Length = longitudinal dimension (cm)
Width = transverse dimension (cm) Thickness = sagittal dimension (cm)
The body mass index was calculated using the formula below: [19]
ETHICAL CONSIDERATION
The study subjects were informed voluntary and they may during any part of the study reside from involvement.
The subjects will be anonymous and we will code the test results and survey together and have that tied to their name so we can give them the results of the test if they want it. In some cases, we have to remove from the research group because they don’t have a normal size of thyroid volume or have nodules and cysts in their thyroid gland.
An ethical self-examination was performed according to the form “Ethical Considerations for Student’s Thesis” at the School of Health and Welfare in Jönköping [appendix 1].
RESULT
A total of 210 participants were examined in this study. In the process of gathering research data, we found that some cases have large volume and thyroid nodule in two lobes, some cases have many cysts in thyroid gland. There are some of the most common thyroid disorders. So we remove from the research group. And results remaining 204 valid samples. The 204 subjects studied consist of 150 (73.53%) females and 54 (26.47%) males.
The results show that, the mean total thyroid volume was 7.44 ± 2.09ml. Maximum volume was 14.57ml and minimum was 3.51ml. Right lobe volume was 4.07± 1.13ml while left lobe volume was 3.38 ± 1.03ml. Right lobe volume is significantly higher than the left lobe (p<0.0001). Maximum right lobe volume was 7.63ml and minimum right lobe volume was 1.77 ml. Maximum left lobe volume was 7.31ml and minimum left lobe volume was 1.64 ml. Correlation between total thyroid volume with the elements:
- Correlation with sex: The thyroid volume between female and male is different. The thyroid volume of male have a greater tendency of female.
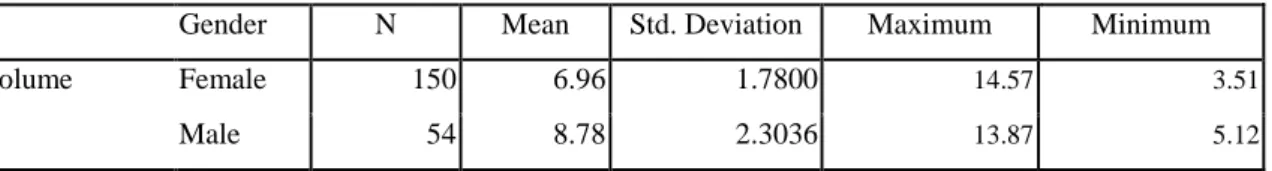
Table 1: The thyroid volume with sex (n = 204).
Gender N Mean Std. Deviation Maximum Minimum
Volume Female 150 6.96 1.7800 14.57 3.51
Male 54 8.78 2.3036 13.87 5.12
The mean volume of male was 8.78 ± 2.30ml for female it was 6.96 ±1.78ml. The thyroid volume of male have a greater tendency of female. (table 1).
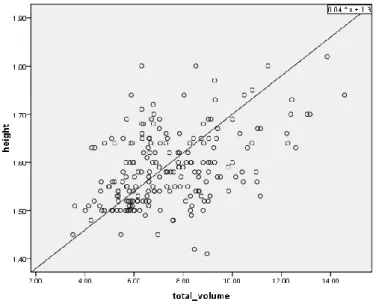
- Correlation with weight and height: The total thyroid volume have correlation with linear regression. And in our study, thyroid volume was best correlated with height (r=0.44; p=0.001)
Figure 3: Relation of thyroid volume with height (n = 204).
The correlation coefficient r = 0.44, the total volume of thyroid gland best correlated with height. Linear relationship a straight line and regression equation is y = 0.04x + 1.3 (figure 3)
Figure 4: Relation of thyroid volume with weight (n = 204).
The relation of thyroid volume with weight is a linear relationship. Linear relationship a straight line and regression equation is y = 4.8x + 18 with r= 0.38 (figure 4).
- Correlation with an area of skin: The correlation coefficient r = 0.43, so the total volume of thyroid gland correlated with body surface area (p=0.001).
Figure 5: Relation of thyroid volume with BSA (n = 204).
The correlation coefficient r = 0.43, so the total volume of thyroid gland correlated with body surface area. Linear relationship a straight line and regression equation is y = 0.096x + 0.76 (figure 5).
- Correlation with body mass index: the correlation coefficient r = 0.14, so in this study the volume of thyroid not correlated with body mass index .
In our study, the mean of BMI is 19.42 ± 2.04 and the maximum value is 26.77, the minimum value is 14.50
The WHO regards a BMI of less than 18.5 as underweight and may indicate malnutrition, an eating disorder, or other health problems, while a BMI equal to or greater than 25 is
considered overweight [according WHO]. So, we have the following table about statistic of BMI in our study.
Table 2: statistic of BMI
Frequency Percent
Valid Skinny 54 26.5
Normal 147 72.1
Overweight 3 1.5
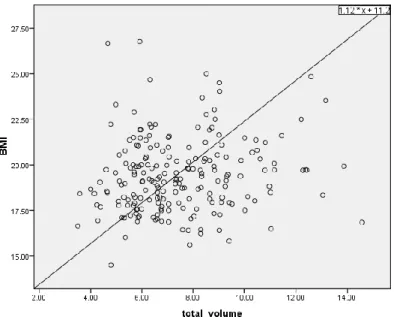
Figure 6: Relation of thyroid volume with BMI (n = 204).
The volume of thyroid haven't correlation with body mass index. The correlation coefficient r = 0.14, the regression equation is y = 1.12x + 11.2 (figure 6).
DISCUSSION
The total thyroid volume: There have been many studies worldwide to determine thyroid
size. However, the published results are very different. According to the European people and the WHO, thyroid volume from 18-25ml (or 18-25g, because thyroid tissue density close to 1), the Japanese is 19ml. If calculated according to body weight is accounted for 0.029% of thyroid [20, 21]. In Vietnam has several studies been published and the data is not uniform. Ha Linh Luong and Mai Trong Khoa volume in 2001 was 2.06 ± 4.07ml thyroid (n = 356), while according to Nguyen Duc Ngo (1996) is 13.72 ± 3.70ml [20].
Total thyroid volume and sex: We found a difference in thyroid volume between male and
female. And the thyroid volume of male have a greater tendency of female.
Total thyroid volume and height: We also found the correlation between total thyroid
volume and height of the individual. Linear relationship a straight line and the regression equation is: y = 0.04x + 1.3 (r=0.44). This observation is similar to the study done by Ivanac G et al. [22] In their study, thyroid volume was best correlated with body height (r=0.37).
Total thyroid volume and weight: In our study, the total thyroid volume was low correlated
with weight of the individual (r= 0.38). The regression equation is: y = 4.8x + 18. This finding is in consistent with the finding of Hegedus Let al [23] Ramazan Sari et al [24] and Svensson J et al [22]. In the study done by Hegedus L et al, the difference in total thyroidvolume between male and female was solely explained by weight [23]. There was a positive
correlation between the changes of thyroid volume and the change of body weight (r=0.341) in the study done by Ramazan Sari et al [24].
Total thyroid volume and Body surface area (BSA): In our study, the total thyroid volume
was correlated with body surface area. The total thyroid volume increased with increasing body surface area and linear relationship a straight line. The regression equation: y = 0.096x + 0.76; similar observations were made by Svensson J et al [22].
Total thyroid volume and Body Mass Index (BMI): We not found the correlation of total
thyroid volume with body mass index. The correlation coefficient is r=0,14 and the equation regression: y = 1.12x + 11.2
This observation is not similar to that found by Ramazan Sari et al [24]. In their study, there was positive correlation of total thyroid volume with BMI (r=0.504).
We are thinking that, in this group of young adults length and weight doesn't have so much influence on the thyroid volume. To learn more about if one can see any changes in volume depending on length and weight we must examine a lot more people of different age and size.
Our thoughts about the role of the radiographer:
The global demand for medical imaging examinations has been growing rapidly over the past decade, especially for ultrasound exams. Some countries have filled the gap by allowing radiographers to perform and interpret ultrasound examinations independently, to relieve the pressure on the staff. In several EU countries, radiographers perform US-based musculoskeletal, urogenital and gastroenterological examinations, as will be shown during the session. The Radiographers' skills, in ultrasound, differ according to the country and the basic formations [European Society of Radiology- ECR gives platform to radiographers in ultrasound management debate].
In Viet Nam, currently, ultrasound is a diagnostic exam performed by medical doctors. The Radiographers, based on their training, also have some knowledge on this area, acquiring skills in order to perform such exams. However, several factors such as legislation preclude their professional activities, including that exists in that country or the lack of authority to certify the skills of Radiographers. The demand for sonographers in some local hospitals and medical centers in Viet Nam has been growing, even there is no radiologist in imaging diagnostic department in some medical centers.
The specialized ultrasound training for Radiographers is suitable for performing ultrasound and if health authorities are able to certify these professionals if they fulfill the number of
and the completion of a graduate diploma. But, in Vietnam there are currently no specialized schools and specialized training courses for bachelor's ultrasound image, while many hospitals and health centers still lack a lot of people who perform ultrasound. Moreover, there are many technicians and engineering bachelor's desired image and loved by ultrasound. In some European countries, schools and training courses for ultrasound technician longstanding. We hope the future and certainly Vietnam will also apply this approach because the demand is there and the ability to meet the quality that is if we are training in a professional manner as follows:
Divided into many areas of ultrasound (Specializations) include:
General abdominal (Abdominal) - these include urinary tract, pancreas, kidneys, liver and spleen among others. Breasts (Breast) - screening or diagnostic. Heart (Echocardiography) - The assessment of the blood flow and anatomy of the heart, valves and blood its vessels. Obstetrics/Gynecology - One of the more commonly thought of ultrasound, this includes keeping track of scanning and fetal growth and development alongside. Evaluating and diagnosing more general gynecological problems. Vascular Technology - Assessment of the blood flow in the abdominal and peripheral blood vessels. Selection each ultrasonic fields to train and in every course in each area, we need to be equipped with knowledge on: Anatomy and physiology and some related abnormalities. And preserved using ultrasound (how to use it and maintain). Scanning methods and techniques. Results presentation ( how to complete patient medical records and reports). The technicians at the bedside and how to care for patients ultrasound (Beside Manner and quality patient care providing)
We think if we follow the process of training in a professional manner, then professional future for ultrasound technicians will succeed.
CONCLUSION
We conduct research with purpose to better understand processes of scientific research as well as to test the research results of the previous authors did.
Knowledge about the size of the thyroid gland is important in following the thyroid diseases and the examination of the gland.
The radiographer's role is very important in determining the volume of thyroid. Through this study, we want to emphrase the role of radiographer. Radiographer is an important member of the diagnostic health care team. They are responsible for producing high quality medical images that assist medical specialists and doctors to diagnose or monitor a patient's injury or illness.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I would like thank the School of Health and Welfare, Jonkoping University and Da Nang University of Medical Technology and Pharmacy for creating conditions for me to perform and complete this study. I am grateful to the two principals of School of Health and Welfare and Da Nang University of Medical Technology and Pharmacy has accepted me to join this course. I also thank for the help of the ultrasound department in Da Nang University of Medical Technology and Pharmacy and the center quality of measurement technique Da Nang city have helped me complete the data collection.
I would like to thank Mr. Thomas Ehn and Dr. Vo Ho Quynh Nhu have supported, encouraged and helped me to complete our study.
Finally I would like to thank Mr. Nguyen Minh Son and Dr. Huong for helping me complete the analysis and resolution of the data.
REFERENCES
1. Marieb & Hoehn, Human Anatomy and Physiology; for anatomical drawings and details of thyroid’s effect on specific body systems; 620-21.
2. Thyroid ultrasound, U.S National Library of Medicine [internet]; 2014 [cited 2015May 1]. Available at:
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003776.htm
3. Solbiati L, Charboneau JW, Osti V, James EM, Hay ID; The thyroid gland. In: Rumack CM, Wilson SR, Charboneau JW, editors; Diagnostic Ultrasound. 3rd ed. Vol. 1. St. Louis, Missouri: Elsevier Mosby; 2005. pp. 735–70.
Available at:
http://ttytdpdt.gov.vn/C%C3%B4ngtr%C3%ACnhkhoah%E1%BB%8Dc.aspx 5. Schlumberger M, Catargi B, Borget I, et al for the Strategies of radioiodine ablation
in patients with low-risk thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:1663-1673. Available at:
http://www.headandneckcancerguide.org/adults/cancer-diagnosis treatments/diagnosis/imaging/
6. Mallick U, Harmer C, Yap B, et al. Ablation with low-dose radioiodine and thyrotropin alfa in thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:1674-1685.
7. What is a thyroid ultrasound [internet], Health line; 2014 [cited 2015April27]. Available at: http://www.healthline.com/health/thyroid-ultrasound#Follow-Up5 8. What is General Ultrasound Imaging, General Ultrasound [internet] June 23,2014.
Available at: http://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=genus
9. What is a thyroid ultrasound, Ultrasound Thyroid [internet]; 2013 [cited April 27, 2015]. Available at: http://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=us-thyroid 10. Basic Ultrasound Physics [internet]. Jun 2, 2012. Available at:
http://www.wikiradiography.net/page/Basic+Ultrasound+Physics
11. PhD. Hoang Ngoc Chuong, Dr. Truong Thi Hoang Phuong. Ultrasound technique [internet]. Education publisher, 2011.
Available at: http://sachviet.edu.vn/threads/ky-thuat-sieu-am-nxb-giao-duc-2011-hoang-ngoc-chuong-86-trang.19088/
12. Luong Linh Ha. Research by ultrasound and thyroid patients Basedow [internet]. Master Thesis Medicine, Ha Noi, 2001. Available at:
http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/70715/1/WHO_NUT_94.6.pdf
13. Thyroid Cancer Treatment–Patient Version (PDQ®); General Information About Thyroid Cancer
14. Vikas Chaudhary, Shahina Bano.Indian J Endocrinol Metab. Thyroid ultrasound [internet], 2013 Mar-Apr. Available at:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3683194/
15. Nghiên cứu đặc điểm hình ảnh,thể tích tuyến giáp người bình thường và bệnh nhân
basedow bằng siêu âm, xạ hình, cắt lớp vi tính [internet]; Available at:
http://thuvienykhoa.vn/chi-tiet-tai-lieu/nghien-cuu-dac-diem-hinh-anhthe-tich-tuyen- giap-nguoi-binh-thuong-va-benh-nhan-basedow-bang-sieu-am-xa-hinh-cat-lop-vi-tinh/2450.yhoc.
16. Robert M. Sargis MD, PhD. Thyroid Gland Overview. A Major Player in Regulating Your Metabolism [internet]. Available at:
17. Ultrasound – Thyroid. [internet]; May 29, 2015. Available at:
http://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=us-thyroid
18. Ghervan C. Thyroid and parathyroid ultrasound. Med Ultrasound 2011; 13: 80–4.
19. Rahman SA, Adjeroh D (2015) Surface-Based Body Shape Index and Its
Relationship with All-Cause Mortality [internet]; PLoS ONE 10(12): e0144639. Available at:
http://www.realclearscience.com/journal_club/2015/12/30/a_new_potential_replacem ent_for_body_mass_index_109492.html
20. Geneva, Indicator for assessing iodine deficiency disorders and their control through salt iodization [internet]; WHO/UNICEF/ICCIDD. WHO, 1994. Available at:
http://text.123doc.org/document/2082013-bao-cao-y-hoc-xac-dinh-kich-thuoc-tuyen-giap-bang-sieu-am-tren-nguoi-binh-thuong-truong-thanh-ppt.htm
21. Ivanac G, Rozman B, Skreb F, et al. Ultrasonographic measurement of the thyroid volume, Coll Antropol.2004; 28(1):287-91.
22. Svensson J, Nilsson PE, Olsson C, Nilsson JA,Lindberg B, Ivarsson SA.
Interpretation of normative thyroid volumes in children and adolescents: is there a need for a multivariate model? Thyroid. 2004Jul;14(7):536-43.
23. Daniels GH. Physical examination of the thyroid gland. In: Braverman LE, Utiger RD, editors. Werner and Ingbar’s The thyroid: A fundamental and clinical text.6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: JB Lippincott Co; 1991. p.572–7.Wiley (2002), Principles of anatomy & Physiology, 10th edition, Tortora and Grabowski, p 603-608.
24. Sari R, Balci MK, Altunbas H, Karayalcin U. The effect of body weight and weight loss on thyroid volume and function in obese women. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2003 Aug; 59(2):258-62.
![Figure 2: This is the ultrasound machine used in study [photo by Dr.Vo Ho Quynh Nhu].](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/5dokorg/5571401.145591/12.892.106.445.592.972/figure-ultrasound-machine-used-study-photo-quynh-nhu.webp)