Page 1 of 5
FRAMEWORK FOR EVALUATION OF STRATEGIES FOR
POOLING OF REPAIRABLE SPARE PARTS
Driton Muhaxheri
[driton.mu@gmail.com]
May 2010
Department of Industrial Management and Logistics,
Lund University, Faculty of Engineering
SE-221 00 Lund, Sweden
This article is based on a Master’s Thesis written in 2009/2010 at Lund University, Faculty of Engineering, in collaboration with the company Systecon AB. The purpose of the thesis was to emphasize different pooling strategies, and to develop a framework that facilitates a fair comparison between considered spare parts strategies. In particular, soft values of each strategy are treated, and subsequently put in relation to the annual cost of a strategy in a final model. A copy is available from the author upon request.
ABSTRACT
The framework presented in this thesis evaluates four spare parts strategies; stand alone, ad hoc cooperation, cooperative pooling, and commercial pooling. Characteristics of all strategies are emphasized and assessed. From the characteristics, which are illustrated in a matrix in Table 1, a model to evaluate soft values of each strategy is derived. The model, named evaluation of soft values, is provided in Table 2 and Table 3. Also, a methodical approach to derive a final strategy is provided in section 5.7 in the thesis.
To make sure that a decision-maker is well aware of how the model should be applied, a fictitious case study is build up in where every step of the decision making process is
thoroughly described. Furthermore, in the case study a final model that facilitates the derivation of a best strategy is presented. The outcome of the final model is based on the outcomes of the cost models and the outcomes of the evaluation of soft values model.
BACKGROUND
It is vital to quickly provide parts for the supply of advanced technical systems in equipment-intensive industries (such as airlines and nuclear power plants) for the systems overall performance.
In order to maintain a targeted system availability large quantities of spare parts are often required which in turn results in excessive inventory costs. Seeing as inventory
Page 2 of 5 systems often account for a large proportion
of a business’ costs a tough issue faced by companies in these industries is how to reduce the total inventory cost without having a negative impact on the system availability. An approach that may successfully deal with such a problem is pooling. Pooling refers to an arrangement in which multiple owners of the same type of technical systems cooperate by sharing their inventories.
METHODOLOGY
The initial phase of the thesis was dedicated to a desk study review of current literature within the field of study. Recently published scientific articles, papers authored by consultants at Systecon, and literature used in courses at the Faculty of Engineering at Lund University lay the basis for the theoretical framework.
The framework, which is developed from explanatory and normative reasoning, is derived from discussions with the supervisors in connection with interviews carried out with; relevant Systecon customers and company representatives at two trade fairs, Offshore Wind 2009 and Nordic Rail 2009.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS
Different strategies can be applied when companies choose to pool their inventory. Kilpi et al. (2008) specifies cooperative strategies for the availability service of repairable aircraft components (ad hoc cooperation and cooperative pooling). Another feasible strategy that can be applied is commercial pooling, where a third party provides the pool of spare parts.
Figure 1 illustrates a distribution system where lateral transshipments between three locations are applied.
Figure 1: Lateral transshipments between three parallel locations (Olsson 2007).
In order for an independent company to pool its inventory the benefits from joining a pool must be larger than from acting alone. When choosing a cooperative pooling strategy, the locations also pool their risk, reduce their inventory level or achieve higher availability in their technical systems. The benefits
mentioned above are mainly derived from having lesser amount of spare parts in the total network system compared to the sum of spare parts of each company that act
independently. Due to scale economies with a pool the investment cost can get reduced and owing to stochastic failure rates the
probability for more than one item-failure at the same time is very low, leading to the ability for a pool to maintain high availability towards all customers.
There are obviously vast benefits that can be derived from pooling, why the obstacles of attaining such a model need to be
investigated and overcome.
Two primary prerequisites for pooling are; the necessity of having at least one more company using similar technical systems (e.g. aircrafts, rail vehicles etc) within a geographical area in where it is feasible to share spare parts, and also, the value of the spares a company chooses to repair must constitute the main part of the total value of all the components in the system.
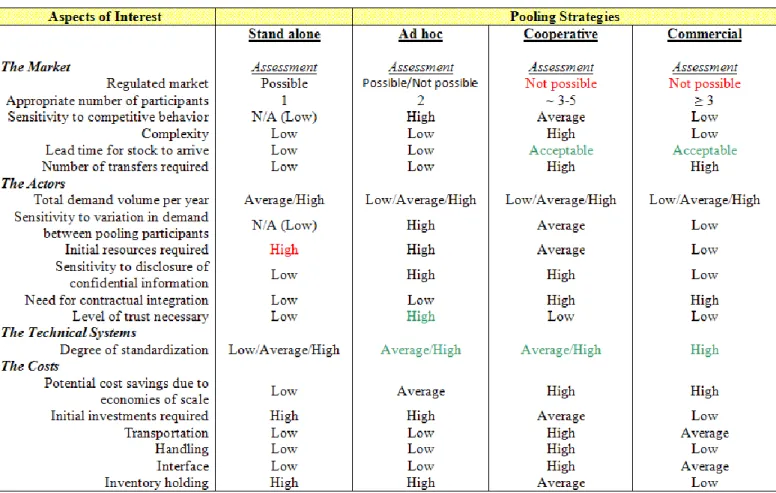
Page 3 of 5 Aspects of interest that need to be accounted
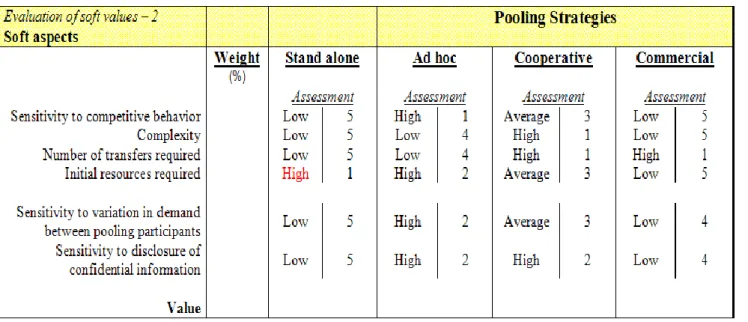
for when a company decides to pool its inventory or not are divided in four categories; the market, the actors, the technical systems, and the costs. Identifying and mapping out all relevant aspects provide a company with fundamental information in deciding whether to pool or not, and more specifically, what spare parts strategy to choose. The aspects are gathered in the matrix in Table 1 below. The first part of the evaluation of soft values model, provided in Table 2, covers main aspects that need to be considered when choosing a strategy. The second part, provided in Table 3, introduce an approach to convert the assessments of other relevant soft aspects into numbers. In so doing, the decision-making process is supported by numerical values.
A methodical approach to derive a best spare
parts strategy is as follows;
1.
Study the characteristics in Table 1 to get a holistic view of what the four strategies might necessitate.2.
A thorough analysis of the main aspects in Table 2 makes way for an exclusion of strategies that are not possible to implement.3.
The soft value of all feasible strategies is then obtained with the help of the second part of the evaluation of soft values model in Table 3.4. Results from the evaluation of soft values model are then weighted against the annual cost in a final model (The final model is provided in Table 6.4 in the thesis).
5. A straight comparison of considered strategies’ final index is now possible.
Page 4 of 5 In order to successfully implement a spare
parts strategy an organization needs access to; reliable software tools, relevant logistical information, and logistical know-how. The software tools necessary to effectively manage a company’s assets comprise information technology (IT) and inventory management systems. An organization must strive to gain a deeper understanding and better knowledge of its technical systems. Valuable logistical information will then be used as input in decision support tools, and consequently, lead to more trustworthy analysis. Upon acquiring a technical system (e.g. a ship, an airplane, an oil platform, a train etc.) a basic condition is that an organization
also ensures logistical information from the supplier. An organization must acquire logistical know-how to set the right requirements on the supplier in order to ensure that important information is provided. Subsequently, the organization need to, among other important actions, build a successful support organization, ensure that it gets correct spare parts, ensure that it uses reliable software tools (e.g. tools that uses good mathematical models).
A common situation is that an organization does not hold resources in-house (software tools and logistical know-how) to carry out advanced optimization analysis. It will Table 2: The first part of the evaluation of soft values model. By studying the main aspects and their
assessment for each strategy a decision-maker may exclude strategies, and hence, continue to evaluate remaining feasible strategies
Table 3: The second part of the evaluation of soft values model. The written assessments are given numerical values, and by this means, enables a decision-maker to assess the strategies numerically.
Page 5 of 5 therefore need to acquire a service that
covers both decision support tools and logistical expertise.
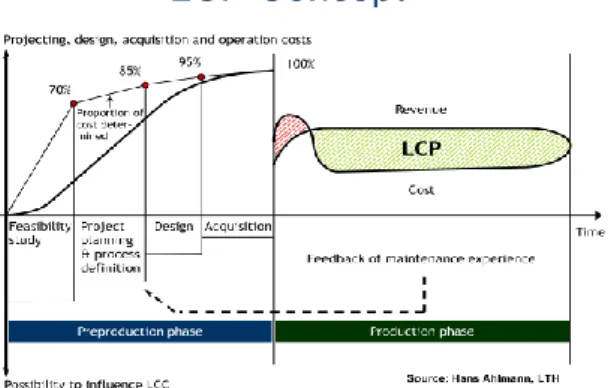
It is desirable to use the framework in the initial stages described in the LCP concept in Figure 2 (e.g. in planning and process definition), seeing as the possibility to influence LCC/LCP are still high. However, the framework may still possess a value-adding effect even if it is applied at the later stages. For example, using the framework developed in this thesis after a final strategy is chosen can benefit a company as follows;
The company can confirm that the selected strategy derived by other means is the right strategy, seeing as the decision is supported based on further analysis.
Seeing as many aspects of interests are covered, the company has the opportunity to reflect on those aspects not taken into account in their model. If necessary, there may still be time left for further modifications. Seeing as reflections are incredibly
important when improving a model or a method, a thorough analysis carried out with the framework provided may lead to a rise in quality in the way the company carry out their own analysis.
Figure 2: The LCP Concept. We note that during the initial stages the majority of the capital will get restricted, and consequently, in these stages the
possibility to influence the LCC is highest (Ahlmann et al. 2010).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The Author acknowledges; Professor Hans Ahlmann at Lund University, Faculty of Engineering, Mr. Håkan Borgström and Mr. Pär Sandin at Systecon AB for their valuable contributions to this thesis.
REFERENCES
Ahlmann, H., Borgström, H., 2010. Emerging theories and methods for addressing maintenance issues at the corporate management level. Faculty of Engineering, Lund University, Sweden.
Kilpi, J., Töyli, J., Vepsäläinen, A., 2008. Cooperative strategies for the availability service of repairable aircraft components. Int. J. Production Economics 117, 360-370. Olsson, F., 2007. Modeling lateral transshipments and perishable items in inventory systems, Lund University, Doctoral Thesis.
AUTHOR BIOGRAPHY
D. MUHAXHERI, M.Sc. in Mechanical Engineering at Lund University, Faculty of Engineering.