Faculty of Technology and Society
Department of Computer Science
Master Thesis Project 15p, Spring 2014
Assessing Data Quality of ERP and CRM
Systems
By
Muhammad Azeem Sarwar
Supervisors:
Annabella Loconsole
Examiner:
2
Contact information
Author:
Muhammad Azeem Sarwar E-mail: azmsrwr@gmail.com
Supervisors:
Annabella Loconsole
E-mail: annabella.loconsole@mah.se
Malmö University, Department of Computer Science.
Examiner:
Helena Holmström Olsson
E-mail: helena.holmstrom.olsson@mah.se
3
Abstract
Data Quality confirms the correct and meaningful representation of real world information. Researchers have proposed frameworks to measure and analyze the Data Quality. Still modern organizations find it very challenging to state the level of enterprise Data Quality maturity. This study aims at defining the Data Quality of a system also examine the Data Quality Assessment practices. A definition for Data Quality is suggested with the help of systematic literature review. Literature review also provided a list of dimensions and initiatives for Data Quality Assessment. A survey is conducted to examine these aggregated aspects of Data Quality in an organization actively using ERP and CRM systems. The survey was aimed at collecting organizational awareness of Data Quality and to study the practices followed to ensure the Data Quality in ERP and CRM systems. The survey results identified data validity, accuracy and security as the main areas of interest for Data Quality. The results also indicate that, due to audit requirements of ERP systems, ERP systems have higher demand of Data Quality as compared to CRM systems.
4
Popular science summary
Data is very centric and important ingredient of any computer or information system. The quality of data will dictate the quality of overall system and all the functions of this system. CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system is a type of software system used in organizations to make the sales process of that company easier. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system is another organizational software system that helps an organization to keep track of all its assets and liabilities. This study examined the data quality of an ERP and CRM systems in an organization. We compared the views about data quality of people working with these systems to what experts of data quality say. According to our findings for good quality, the data in a system should be valid, error free and secure. Now we will use these results in future to ensure that ERP and CRM systems have valid, true and accurate data; and only people who should see or change this data are able to see or change this information.
5
Table of contents
1 Introduction... 11
1.1 Problem statement and motivation ... 12
1.2 Research goals ... 13
1.3 Research scope ... 13
1.4 Results ... 14
2 Context of study ... 15
2.1 Products ... 15
2.1.1 Customer Relationship Management system ... 15
2.1.2 Enterprise Resource Planning system ... 16
2.2 CRM Process ... 16
2.2.1 Marketing ... 17
2.2.2 Sales ... 17
2.2.3 After sales support and forecasting ... 18
2.3 ERP Process ... 19
2.3.1 Accounts ... 19
2.3.2 Revenue ... 19
2.3.3 Finance ... 20
2.4 Practices, Tools and Techniques ... 20
2.4.1 CRM and ERP systems architecture ... 20
2.4.2 CRM and EPR systems Integration ... 21
2.5 People ... 22
2.6 Organization ... 24
3 Research method ... 25
3.1 Research methods ... 25
3.2 Research methods selection ... 27
6
3.4 Systematic literature review ... 28
3.4.1 Literature searching ... 30
3.4.2 Obtaining and assessing ... 30
3.4.3 Review method ... 31
3.4.4 Reading... 31
3.4.5 Critical evaluation ... 32
3.4.6 Recording ... 32
3.5 Data Quality Assessment Survey ... 33
3.5.1 Defining the survey ... 33
3.5.2 Survey planning and design ... 34
3.5.3 Survey Execution ... 36
3.5.4 Survey limitations ... 36
3.6 Threats to validity ... 36
4 Literature Review ... 38
4.1 Literature base for this study ... 38
4.2 Data Quality of CRM and ERP systems ... 40
4.2.1 Data Quality standing ... 40
4.2.2 Method of DQ definition selection ... 41
4.2.3 DQ definition selection ... 42
4.3 Data Quality Assessment method ... 43
4.4 Practicality of Data Quality Assessment methods ... 44
4.5 Survey parameters of Data Quality Assessment ... 45
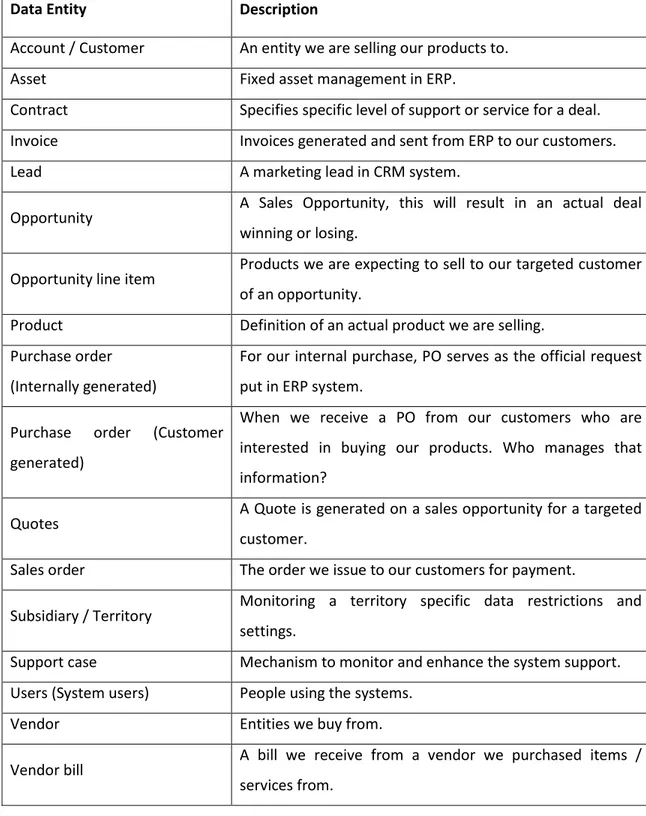
4.5.1 Data Entities selection for study ... 45
4.5.2 Prioritization of Data Quality initiatives ... 48
4.6 Literature review conclusion ... 49
5 Survey Results ... 50
5.1 Objective ... 50
5.2 Survey base ... 50
7
5.3.1 Data Quality and Data management ... 51
5.3.2 Data Entity ownership ... 53
5.3.3 Data entry and validation ... 55
5.3.4 Data Quality Audit and control ... 56
5.3.5 Data Quality Dimension prioritization ... 57
5.4 Evaluation ... 59
6 Conclusion and future work ... 60
6.1 Discussion and Conclusion ... 60
6.2 Benefit to the company under study ... 61
6.3 Answer the Research Questions ... 61
6.4 Future work ... 62
References ... 63
Appendix 1: DATA QUALITY ASSESSMENT SURVEY ... 66
Part 1: Data Quality ... 66
8
List of Figures
FIGURE 1:SALES OPPORTUNITY STAGES ... 18
FIGURE 2:CRM AND ERPINTEGRATION ... 22
FIGURE 3:LITERATURE REVIEW PROCESS [17] ... 29
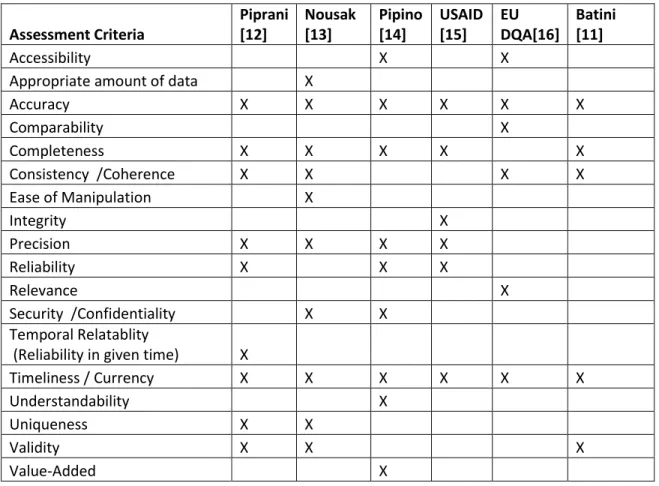
FIGURE 4:RESEARCH AREAS RELATED TO DATA QUALITY [3, P.17] ... 40
9
List of Tables
TABLE 1:JOB FUNCTIONS ... 23
TABLE 2RESEARCH QUESTION TO RESEARCH METHOD ... 28
TABLE 3LITERATURE TO RESEARCH QUESTIONS MAPPING ... 39
TABLE 4:DATA QUALITY DIMENSIONS ... 44
TABLE 5:DATA ENTITIES IN ERP AND CRM SYSTEM ... 47
TABLE 6:DATA QUALITY PRIORITIZATION ... 48
TABLE 7:DATA QUALITY DEFINITION ... 52
TABLE 8:DATA ENTITY OWNERSHIP ... 54
TABLE 9:DATA ENTRY AND VALIDATION ... 55
TABLE 10:CRM AND ERPAUDIT REQUIREMENTS ... 56
10
List of acronyms
ERP Enterprise Resource Planning
CRM Customer Relationship Management
DQ Data Quality
DM Data Management
MDM Master Data Management
ER Entity Resolution
DQA Data Quality Assessment
11
1 Introduction
Data is gradually becoming an organizational asset [1], more valuable than any other preserved or perishable asset. Organizations start to realize that to survive in a connected global economy where global boundaries do not put any restriction on the customers; they have to make informed decisions to stay in business. An up to date, connected and skillfully crafted knowledge base is the basis of all informed decisions. An organization have to change its business process in response to the changing business needs but one part of the processing stays unchanged, data. Due to the long-term business prospects and impacts of data organizations are spending a lot of resources to extract, transform and utilize data.
Data has always been considered a brainchild of humankind but the technological advancements in computing have created new ideas like ‘The internet of things’ [19]. In these computing models data is generated and utilized not only by humans but also by machines. The traditional communicate forms will expand to human, human-thing and human-thing-human-thing [19]. Radio Frequency Identification techniques (RFID), Near Field Communication (NFC) and many similar technologies are enabling seamless and effortless collection of data. This automated data collection makes the business processing smoother than ever before.
At the same time more and more business processes are becoming candidate for automation. Several computer systems and automations are deployed in the companies. As the electronic existence of organization matures, it creates many independent and isolated knowledge bases; we can refer to these knowledge bases as data islands. Each data island contains valuable information related to its domain as well as other meta-information and trivial meta-information. Once the users of a system realize that they can benefit from a piece of information hosted by a different system, they ask for integration between two systems. It does not take very long to have a web of interconnected information systems connected through different means of integrations [20].
12
A data warehouse with vast amount of data and systems owning this data creates a valuable source of information for an organization, at the same time the difficulty of organization and management of this information is directly proportional to the size of data warehouse. These information systems are developed with different business needs and these systems are aimed at different domains that can create inconsistent data semantic for business entities once these systems are connected. The study and standardization of these aspects is called Data Quality. [2, p.73]
1.1 Problem statement and motivation
Data Quality has been an interest of enterprise executives from the start of computer usage in industries and business [2, p.3] but recent trend of using data to make the business decisions has put immense pressure on data experts to produce data of very high integrity. The quality of data will dictate the usefulness and trust of overall information system. For instance if an online store promise a discount in product campaign, while this discount is not translated in the actual purchase due to poor synchronization between CRM and ERP systems; it will be enough to damage the customer trust forever.
High Data Quality is not only considered as an extra attribute of a database anymore, rather the growing awareness of Data Quality has led to major public initiatives like the "Data Quality Act" in the USA and the "European 2003/98" directive of the European Parliament [3, p.4]. The standardization of Data Quality is a research work in progress by ISO. Data Quality standard ISO 8000 will help organization to standardize the data quality across all domains [4]. At the time of writing, this standard is still in development and no guidelines are available for its use.
A CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system hosts the information of current and future customers of an organization. A CRM system stretches from Marketing, where campaigns are designed and future customer leads are generated. CRM system will then help the sales process to convert a marketing lead to an actual sales opportunity. CRM system will keep on hosting the after sales customer and support information.
An ERP (Enterprise resource planning) system is more close to the actual services and production line than a CRM system. An ERP system can be categorized as management software where planning, costing and development tasks are hosted. Once a sale
13
opportunity is materialized in CRM system, this information is passed to ERP system. ERP system then inventories the sales against physical stock in warehouse.
Enterprise Data Quality requirements and lack of an established Data Quality assessment method are the biggest motivations for this study. We will incorporate the existing findings in this field and use Data Quality assessment methods proposed by other researchers to measure the Data Quality of two connected CRM and ERP systems. The study will see how well these systems adhere to Data Quality standards. In the last part of this study we will generalize these finding for contemporary data quality issues.
1.2 Research goals
The main objective of this study is to analyze the Data Quality issues associated with information systems implementation. This study will identify the gaps and problem areas with current information system implementations and analyze the factors making it harder for organizations to recognize and adapt to Data Quality best practices. The expected outcome of this study is an analysis report of understanding and assessment of Data Quality.
This study will focus on answering following research questions:
RQ1: How the Data Quality of CRM and ERP system is defined? RQ2: How a method for assessing Data Quality can be defined?
RQ3: How well the Data Quality assessment methods work in practice?
1.3 Research scope
The scope of this study is bound to the study of Data Quality standards compliance of an organization. We will execute the study on Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems of a public limited company selling products to support Business Intelligence.
14
1.4 Results
This study will list the implementation constraints responsible for any quality issue. The survey results will give us an empirical view of Data Quality assessment methods feasibility and see their viability for CRM and ERP systems.
15
2 Context of study
The purpose of this chapter is to present the organization and functionality of CRM and ERP systems and processes in our organization under study. This chapter will set the empirical perspective for this study. The contents of this chapter are writer’s experience with the organization and ERP and CRM systems.
This chapter will give a brief introduction of the organization where we are conducting this study. After the introduction we will explain the function of CRM and ERP system in our organization under study. In the introduction of this study we described a broad functionality of these systems. This chapter will refine the practical steps of CRM and ERP system usage in day to day business and how these systems are connected to each other. We will list different job functions responsible to operate these systems.
The context description will follow the guidelines set by Petersen [23] to describe the context of industrial software engineering in research. According to this guideline a case organization is described by its Products, Processes, Practices, Tools, Techniques, People, Organization and Market.
2.1 Products
We are going to use ERP and CRM system of QlikTech in this study as objects of research. In the introduction of this study we described a broad functionality of CRM and ERP systems. To set a context for this study we will explore these products in more detail.
2.1.1 Customer Relationship Management system
A CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system hosts all the data, processes and business logic for current and future customers. A CRM system will use technology to automate and synchronize different departments in an organization dealing with customers. For instance marketing, sales, customer service and after-sales service departments depend heavily on the validity of information in CRM system.
16
To support the financial and product growth of QlikTech, we need firm, flexible and extendable CRM systems in place. QlikTech is using Salesforce as organizational CRM system due to its cloud based, on-demand and extendable service. To avoid any confusion with system names we will not use the system provider name and we will use CRM as a generic term to refer the salesforce CRM implemented in QlikTech.
2.1.2 Enterprise Resource Planning system
An ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system is collection of services and automation to automate, monitor and track the resources of an organization. Contrary to the function of a CRM system, an ERP system is close to the organization and list all the services and products to sell as well as keeps track of internal assets of the organization. We can say that ERP is backend of CRM system, where CRM system and its functions are more visible to outer world than an EPR but all the processing of sales transitions initiated by a CRM is not possible to execute without an efficient ERP system at the backend.
To support the financial and product growth of QlikTech, we need firm, flexible and extendable ERP systems in place. QlikTech was using Microsoft Dynamics ERP until July 2014. Due to the limitations in the architecture of Dynamics ERP, another cloud based ERP system Netsuite is now chosen as enterprise ERP for QlikTech. To avoid any confusion with system names we will not use the system provider name and we will use ERP as a generic term to refer the Netsuite ERP implemented in QlikTech.
2.2 CRM Process
CRM system is operated by Marketing, Sales and Support departments, so CRM processes follows these working of these departments. In the following paragraphs we will break down the functionality of CRM by different departments of an organization using this system. First we will give the reasoning of use then we will brief that how a CRM is used in certain department.
17
2.2.1 Marketing
The marketing department is responsible for bringing in the customers for business. There are usually two methods followed in the organization under study, 1) Direct marketing and 2) Alliance marketing.
Direct marketing is a major marketing strategy used by businesses of all sizes, where a target audience is selected and through an organized marketing method company message is delivered to this audience. The CRM system helps us to reach target audience via Email marketing campaigns, Social media marketing campaigns and direct phone marketing. All these marketing transactions are recorded in a centralized CRM system so people working in different teams and locations have access to up-to date marketing status of any customer.
Alliance marketing is a mean where other businesses pool together their client resources and share the potential customer information. Alliance marketers have a limited access to our CRM and ERP system where they can register this information. If a customer is introduced by an alliance partner and that customer actually buys the product then alliance partner is given a predetermined share of the revenue. This revenue distribution is tracked using ERP system.
For both Alliance and Direct marketing CRM system will host marketing information starting as “Marketing lead”. Marketing lead is the initial entry point of a potential customer in the system. Once a marketing lead is realized to have the potential of an actual sale then it is converted to a “Sales opportunity”, at this point marketing department hands over the transaction to Sales department.
2.2.2 Sales
Sales department is responsible for selling the product and bringing in the revenue. Once a “Sales opportunity” is created in CRM system then sales department takes over the process and starts a one to one coordination with the customer. A sales opportunity goes through different phases of sales. Following diagram 1 gives a transition of opportunity status during a sales cycle. These stages indicate the maturity of a single sales instance at any given time in CRM system. Figure 1 is constructed as the writer’s working knowledge of CRM system in the company.
18
Figure 1: Sales opportunity stages
“Goal Identified” is the first stage of opportunity registration where a customer is realized as a prospective buyer of the product. The next stage is either “Goal confirmed” or “Goal rejected” that decides if it possible to proceed with this opportunity. If the opportunity goal is confirmed then “Negotiation” stage is started where all the sales deal is negotiated and finalized with the customer. At the end, if the opportunity results in a successful sale then it are marked as “Closed Won” otherwise it is marked as “Closed lost”. Finance department can intervene at any time during the sales transition and reject the sale due to any legal or financial matter.
2.2.3 After sales support and forecasting
After sales support phase starts once a sales deal is through and customer has purchased the product. Using the same CRM system customers can register their support requests and sales department can delegate those requests to related departments.
One more important sales step called product forecasting is performed at this level and all the sales data and customer history is used to analyze and predict the future sales and
Goal
Identified
Goal
Confirmed
Negotiation
Closed
Won
Closed Lost
Finance
Rejected
Goal
Rejected
19
sales potential with an existing customer. Forecasting module is part of CRM system and helps Sales and marketing department to streamline the future strategy.
2.3 ERP Process
ERP is managed and operated by Accounts, Revenue and Finance departments, so all ERP processes follow the operation of these departments. In the following paragraphs we will break down the functionality of ERP by different departments of an organization using this system. First we will give the reasoning of use then we will brief that how an ERP is used in certain department.
2.3.1 Accounts
The accounts department manages and monitors all head of accounts in the organization. Accounts department records accounts-payable and receivable, payroll, fixed assets, inventory and all other financial elements.
An ERP system is the main system of use in accounts department. ERP will hold all the accounts information for internal assets and liabilities. To facilitate the accounts department and to reduce the aspect of human error in financial figures, ERP has automated some tedious accounting tasking for example automatic revenue recognition entries and assets depreciation entries.
2.3.2 Revenue
Revenue department is the bridge between CRM and ERP systems. Once a sales opportunity is negotiated in CRM and it concludes on a potential sale then a Quote is created in ERP system. A quote details more specific and detailed information about the sale. All that detailed and granular information is only available in ERP system.
This point requires many validations and synchronization of data between two systems. Creating a quote might trigger some approval processes within the organization. These approvals are another way of ensuring the data validity and consistency between both CRM and ERP systems as well as sales adherence to organizational policies and international laws. Once a quote is finally agreed upon and signed by the customer that results in successful sales transaction. This transaction will also set the opportunity status
20
to “Closed won” in CRM system. In case the transaction does not end in a successful sale then opportunity is set to “Closed lost” status.
2.3.3 Finance
Finance department is responsible to assure a smooth revenue flow in the organization. To accomplish the smooth revenue flow Finance has to monitor and audit all the sales transactions happening in the organization. Finance department makes sure that all the financial figures in the ERP system are correct, in this way they support and supplement accounts department to make a stable and auditable ERP system.
The function of Finance department starts from the realization of a customer in CRM where customer background, credit history and other financial constraints are checked. If a Quote is created in the ERP system with special and out of the norm financial terms that requires approval from finance before proceeding to the sales agreement. After the sale transaction finance will invoice the customer and make sure that for a software product a valid license is delivered to the customer and customer is paying as per the agreement.
2.4 Practices, Tools and Techniques
As defined earlier, QlikTech is using Salesforce platform for CRM operations and Netsuite platform for its ERP operations. This section will discuss the architecture of these systems and then we will discuss the details of integration between CRM and ERP systems.
2.4.1 CRM and ERP systems architecture
Traditional CRM and ERP systems were hosting all the functions required for the system in a single piece of software. Organization interested in using these systems were required to host the CRM and ERP systems on a centralized location and all departments were accessing this information from that host. Although this approach gives more control and security over this information; but at the same time this architecture was risking the around the clock availability of a system.
Our company under study is spread globally, so the hosting of a system in one location will cause undesired network delays and the difficulty of system administration around
21
the clock. To see this issue imagine that ERP system is hosted in Sweden while Finance department in Japan is making some big financial transactions in the morning time while people in Sweden are not yet awake. Due to some unforeseen reason the system is not accessible in Japan. This will hold the japan office for many hours until people in Sweden start working and resolve any issue in the system. This whole problem is due to the implementation nature of traditional systems.
Most of the new ERP and CRM systems are aiming to use Cloud computing to deal with these issues. Cloud computing refers to the software delivered as a service as well as on demand supply of hardware resources [18]. These computing solutions are engineered to remove the need of hosting the system in one specific location and giving the autonomy of administration from anywhere in the world.
Both ERP and CRM systems in our organization are using the Cloud computing architecture. It gives the leverage of remote administration and on demand resources acquisition. If any extra space of processing power is required then all of that can be ordered using a single web interface and due to the flexibility of the architecture, a system will get these extra resources within minutes.
2.4.2 CRM and EPR systems Integration
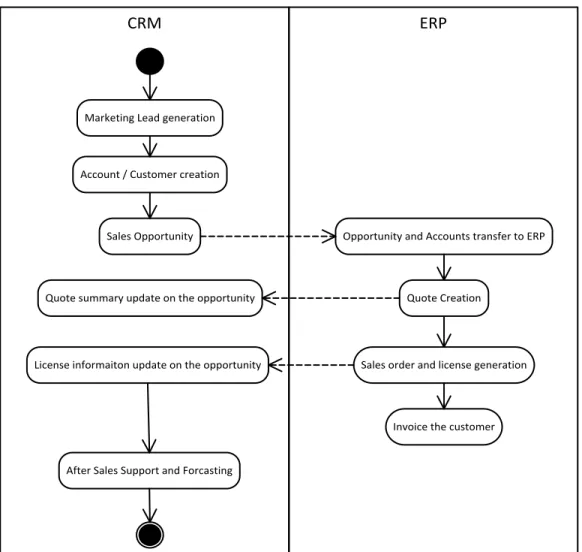
If CRM and ERP system are provided from the same vendor and physically they are part of same software suite then no integration is required between two systems. In our organization under study ERP and CRM are acquired from two different vendors, so these two systems are hosted and work independent of each other. This requires an integration system to be in place to synchronize and control the information in both systems. Figure 2 shows an activity diagram of the integration steps between CRM and ERP systems.
22
ERP CRM
Marketing Lead generation
Sales Opportunity
After Sales Support and Forcasting
Quote Creation Account / Customer creation
Opportunity and Accounts transfer to ERP
Sales order and license generation
Invoice the customer License informaiton update on the opportunity
Quote summary update on the opportunity
Figure 2 : CRM and ERP Integration
The integration between ERP and CRM happens on many levels. When an account is created in CRM system and realized as a potential sales opportunity then account and sales opportunity information is transferred to ERP system. This information will be required to create a quote in ERP system. Once a quote is created in ERP then a summarized version of information is sent back to CRM system that enables sales people to quickly see and analyze quote status for an opportunity.
2.5 People
This section lists all the job functions involved with the operation and implementation of ERP and CRM systems. Each job function is associated with a system that used in their day to day work. Some job functions for instance, the integration experts and finance controllers are working with more than one system in their daily work. The data in
23
Table 1 : Job functions, is constructed with writer’s knowledge of organization under study. The information will help us understand that who is monitoring and controlling the data in the organization. For instance we can see from this table that Sales operations job function is responsible for Administration and execution of sales and CRM is their tool of work.
Table 1 : Job functions
Job function Description Associated systems
Sales operations Administration and execution of sales. CRM
CRM Administrator Administration, maintenance and general support of CRM system.
CRM
CRM Analyst Analyzing the sales process and making sure that CRM system is capable to support the sales and marketing department. They serve as a bridge between business and technical team.
CRM
CRM Developer Responsible to extend the capabilities of CRM system. They usually get their requirements from CRM analyst.
CRM
Integration expert Ensure timely and correct information between CRM and ERP systems.
CRM and ERP
Finance operations Ensure smooth Revenue insurance. CRM and ERP
Account operations Responsible for all account heads and expenses in the organization.
ERP
ERP Administrator Administration, maintenance and general support of ERP system.
ERP
ERP Analyst Analyzing the sales and revenue process and making sure that ERP system is capable to support the accounts and revenue department. They serve as a bridge between business and technical team.
ERP
ERP Developer Responsible to extend the capabilities of ERP system. They usually get their requirements from ERP analyst.
24
2.6 Organization
We conducted this study at QlikTech AB, a software company based in Lund, Sweden. QlikTech provides a series of Business Intelligence (BI) products by the name of QlikView and Qlik Sense. QlikTech was found in Lund in 1993 as a startup with 35 people but now its staff of more than 2000 people is spread over 25 countries. QlikTech reported annual revenue of 470.5 million US dollars in 2013 with an increase of 21%
from 2012. These facts indicate a very high growth rate for QlikTech.
The first reason for selecting QlikTech as an organization to study is the diverse and vast amount of ERP and CRM data in this organization. Customers and offices spread over many continents can give many challenges in data handling and quality. Further Qlik has been using different ERP and CRM systems to reach its current state, so system processes are mature enough to give a good representation of a working system.
The second reason for selecting QlikTech as an organization to study is the writer’s access to ERP and CRM system and process in this organization. A customer repository and internal assets systems are usually not disclosed to any person or authority outside of an organization. Easier access to these systems made QlikTech a good option for this study. Still we are obliged to not share any customer information or internal company information through this study.
The third reason for selecting QlikTech as case organization is the understanding and familiarity of data and data related terms in the organization. QlikTech is manufacturing BI products that reply heavily on Data, so there is a good knowledge of data terms in all the departments of organization. In contrary if we pick another organization working in a different domain then business side of organization may lack the knowledge of technical terms. This factor will render our research more useful.
25
3 Research method
In this chapter we discuss the research methodology used to evaluate candidate Data Quality Assessment methods collected through literature review. This section is divided into four sub-sections. In the first sub-section, the chosen research planning and the reason for choosing this research method is described. In the next part, the systematic literature review method and planned survey is described. In the last section, the evaluation methods which are used for the evaluation of this research are described.
3.1 Research methods
Oates mentioned many strategies for research execution [17 p: 35]. Some strategies are of exploratory nature while other research strategies are of more analytical nature. This study is of analytical nature where existing findings are analyzed to evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of these proposed methods. In the following paragraphs we will discuss different research strategies mentioned by Oates [17] and their suitability for this study.
Literature review serves as the base for any research oriented study. Literature
review ensures that researcher has reviewed the books, articles and other published material to see the standing of other researchers in the area. [17] This evaluation of literature gives an idea about the feasibility of the study as well as the research gaps in existing literature are identified with this review. The new study can help to fill these research gaps. For this study the use of literature review is not only limited to assess the existing research work but we have to give a definition for data quality assessment as well as visit the practical dimensions of DQA (Data Quality Assessment). With these requirements we will use literature review to give us a conceptual framework for this study and we will use systematic literature review to explore all DQA literature for DQA definition and to identify the empirical features of DQA in literature.
26
Survey is a systematic way to collect information of same kind from a large data
source. [17] These data sources can be people, documents, events or electronic data. Usually a survey is executed on a selected sample from the whole population and this sample should be representative of the other individuals in the whole population. In our study we have to collect same type of information from a wider audience, so survey will be our data collection strategy to collect information from domain experts.
Design and creation is research strategy aimed at creating new products, processes
and models [17]. Due to analytical nature of our study this strategy is not suitable for our use.
Experiment is a systematic study of cause and effect. A hypothesis is formed
before the experiment and in a controlled environment predefined process is conducted. The output from the experiment is carefully analyzed to verify or falsify preformed hypothesis [17]. The requirement of controlling the environment and the lack of a set standard for DQA renders experiment unfit as a research strategy for this study.
Case study is a research strategy to focus on a single thing and study all the
characteristics and complex relationship of that single case in detail [17]. In contrast to a survey that is broader but shallow, a case study does not care about the context and try to explore all details of a single case. Although we are considering a single organization for this study we will limit ourselves to the context of DQA of ERP and CRM systems.
Ethnography is a research strategy to study the way of seeing of a particular group
of people. [17] DQ and DQA lies between groups of people, for example a technical person will have a different perspective of DQA as compared to the people working in finance or accounts department. This distribution was more evident from our collected results but at this phase of study we will not explore this ethnography as a research strategy and use it in the future iterations of this study.
27
3.2 Research methods selection
In previous section we iterated different research strategies and briefly discussed the suitability of each method for our study. Runeson discussed the possibility of mixing multiple research methods to enhance the validity of a case study over opting for a single research method as vivid evidence [21]. Stake suggested the use of Triangulation to increase the precisions of an empirical study [22]. Triangulation refers to the approach of taking different perspectives and data sources into consideration, to add to the validity and precision of a qualitative study. Using Methodological triangulation we can combine different data collection methods to collect qualitative and quantitative information and combine that to answer the research questions. [22]
Using Methodological triangulation, we will use systematic literature review as qualitative data collection method and survey as a quantitative data collection method. Systematic literature review will ensure that we are collecting all the data related to this study in a flexible and open manner. Survey will give us controlled and measureable data to testify against the findings of literature review. Information collected with these methods will help us to answer our research questions.
3.3 Research planning
For an industrial study it is recommended to conduct a literature survey of industrial studies to determine to what degree industrial case studies covered the context identified in this study [23]. A systematic literature review will give us a literary base to conduct a survey; this survey will show us how well Data Quality Assessment is practiced against methods proposed by different researchers.
For the sake of validity we are going to limit our study to published research material on Data Quality Assessment. For the selection of relevant and research work we need a basic framework to track and associate our findings from literature review to the research questions of this study. Table 2 gives a mapping of research questions to the research method answering this question. This table is further explained in next paragraphs.
28
Table 2 Research Question to research method
Research question Systematic Literature review Survey RQ1 : DQ of ERP and CRM system X
RQ 2: DQA method definition X X
RQ 3: DQA in practice X X
To answer first research question, “How the Data Quality of CRM and ERP system is defined?” with the help of detailed literature review, we have defined the attributes of a good quality CRM and ERP system. This step gave us a list of attributes and properties of a system that we can monitor in the later part of this study. We will limit the quality parameters for CRM and ERP system, as these are very commonly used systems in organization so any result inferred for these systems can be generalized for other systems. The second research question, “How a method for assessing Data Quality can be defined?” is targeting the Data Quality assessment in general. As we experienced from a literature review that there are many research gaps in Data Quality study. There are not enough specialized models to access the Data Quality of an ERP and CRM system. A detailed literature review gave us an insight in available Data Quality assessment methods. Now we can analyze and study the DQA dimensions in next research question.
We will conduct a survey to answer third research question “How well the Data Quality assessment methods work in practice?” This survey will present the assessment methods identified in previous step to domain experts. For this survey the main strategy will be questionnaires, but it will also use documents, observations and personal experience as extra help in the research process.
3.4 Systematic literature review
Literature review is a systematic way of finding existing work in the research area. It places the research work in context of what has already been published. There are three main aspects in a systematic literature review that makes it systematic [24]
Clarity: the findings should be clear and precise by giving a good account of collected knowledge.
Validity: all the literature should be collected from an authentic and valid source.
29
For the selection of relevant and research work we need a basic framework to track and associate our findings from literature review to the research questions of this study. Later in this section we will discuss this framework of literature work association. Literature review process
Figure 3: Literature review process [17] diagram shows different steps of literature review presented by Oates [17]. The execution of all these steps is discussed in the subsequent sub-sections.
Figure 3: Literature review process [17]
Due to the nature of the subject we will start with a broader perspective of Quality and gradually we will narrow down our finding to Data Quality Assessment method. We will find the existing work to set a standard for Data Quality. With the help of basic Data Quality definition we will map this definition to ERP and CRM systems. This first step will give us an answer to our first research question: How the Data Quality of CRM and ERP system is defined?
The quality standardization established in first step will be handy when we will compare different approaches to match the data and perform comparative analysis of the data quality. This part of research will bring us closer to our second research question: How a method for assessing Data Quality can be defined?
To find the answer of our third research question, we will survey the literature to find the practices of Data Quality Assessment. In the last part of literature review we will
30
review several approaches devised to access the data quality of MDM. We may need to merge different constructs of data quality assessment to form a comprehensive method. Next steps in our research, after the literature review, will prioritize only the most important constructs of selected methods.
3.4.1 Literature searching
Data Quality literature is often published under Data Management headings. Various search terms around Data Quality and Data Management were used to capture maximum published literature. The selection of these keywords was an evolving process where we started with some direct keyword like Data Quality and Data Quality Assessment and in the found literature other keywords used by the researcher gave us indication of related keywords. We kept record of these research terms to avoid duplication of results.
Following keyword are used to find literature for this study: Data Quality, Data Quality assessment, Data Quality measurement, Quality measurement, Data Quality management, Data Quality Monitoring, Data Quality Matrix, Data Quality evaluation, Data Quality Standardization. All keywords were used to collect research material related to all our research questions. After review (described in section 3.4.4) the collected material was distributed for its contribution to answer each research question.
Each search keyword returned 0.75 to 5.34 million hits on the google scholar, with Data Quality with most number of hits (5.34 million) and Data Quality Standardization with the least number of hits (773,000). By looking at the title of the search material we analyzed that after initial 20 to 40 search results retrieved by google scholar the rest of the research results render irrelevant for this study. So, only research papers with a title relevant to this study were obtained in the next phase of literature review.
3.4.2 Obtaining and assessing
To compile the list of supported literature we started our search with Google Scholar, with search terms mentioned in previous section, to find as much related research material as possible. After compiling a generic list of related literature we searched computer science specific research portals like ACM and IEEE with the same research terms. Most of the articles found through these search engines were not publically
31
accessible. We used Malmö university digital library to access these publications and stored the electronic copies for reading and evaluation. After the completion of this step in literature review, based on matching titles, we shortlisted 62 research papers, articles and books for review.
3.4.3 Review method
The findings from previous step were categorized by their contribution to our research questions. We formulated a matrix where each research question was added as a column next to each research paper. This matrix has the dimensions of R x N+1; where R is the number of research articles we collected and N is the number of research questions we have defined in this study.
3.4.4 Reading
After obtaining all literature for this study, each research paper is listed as a single line in the literature review matrix defined in review method. For reviewing an article, first its abstract was visited and if the abstract looks promising to answer any of our research question then this paper was selected for a detailed review otherwise this paper was not considered for further review. 36 research papers were shortlisted after analyzing their abstracts.
Papers listed for detailed study were scanned thoroughly to answer research questions. Small description and the possible reason for selection were noted for each research paper.
Reading for RQ1: After reading the papers, we identified 7 literature items containing the elements of Data Quality definition and can help us to answer our first research question about Data Quality definition.
Reading for RQ2: After reading the papers there were 16 literature items containing the methods and recommendations to assess the data quality of a system. These 16 papers can help us to answer our second research question about Data Quality Assessment method.
32
Reading for RQ3: After reading 14 research papers were discussing the different practical dimension of DQA. This information will help us to answer the third research question on the practicality of DQA methods.
3.4.5 Critical evaluation
We start evaluating all shortlist research paper after reading and marked all the corresponding research question in the matrix, this paper was helping us to answer. An ‘X’ mark in front of research paper under a column for research question RQx will mean that given research paper will help us answer a certain research question RQx. In the end we only selected those research papers those have any research question marked in the matrix and rejected irrelevant research papers.
Critical evaluation for RQ1: To answer the first research question, all the research papers and other literature that contains the elements of defining the Data Quality of a system were selected. There were 7 literature items containing the elements of Data Quality definition. After removing the redundant attributes and only selecting the research papers and literature with direct definition Data Quality, selected papers are limited to 4.
Critical evaluation for RQ2: To answer the second research question, all the research papers and other literature that contains the practices and recommendations for Data Quality Assessment were selected. There were 16 literature items containing the methods and recommendations to assess the data quality of a system. After careful analysis of the practices and only selecting the papers with generic practices targeted at DQA, the number of research papers is limited to 6.
Critical evaluation for RQ3: To answer the third research question, all the research papers that contains the different practical dimension of DQA. Security, accessibly, consistency and integrity are some of the dimension identified by researchers of DQA that we are trying to record. These DQA application dimensions were mentioned in14 research papers. 6 research papers out of these 14 papers are selected for unique dimensions.
3.4.6 Recording
Recording is the step of literature review where the important informant collected after critical evaluation of literature is noted.
33
Recording for RQ1: For our first research question all the attributes of Data Quality definition were noted from the research papers shortlisted in critical evaluation step. These attributes are discussed in literature review chapter.
Recording for RQ2: For the second research question the methods suggested for assessing the data quality of a system are noted. In the next chapter we will examine the selected DQA practices for review and evaluation.
Recording for RQ3: For the third question we listed all the possible dimensions of DQA. Our survey will present these dimension for a review and give an importance index to these dimensions.
The next chapter will discuss the literature review results and will serve as the last step of review process with a critical review.
3.5 Data Quality Assessment Survey
Survey is a systematic way of collecting data from a diverse population. According to Oates [17] there are four stages of a survey 1) Defining survey 2) Planning and Designing surveys 3) Survey execution and 4) Survey results evaluation. We will elaborate each step from this process in coming text.
3.5.1 Defining the survey
The objective of the survey is twofold. One to get an idea that how Data Quality is understood in the organization and if there is a clear ownership of data defined in the organization. Second objective was to see which areas are important for Data Quality in overall system so that future efforts for Data Quality and Data Quality Assessment will be directed on these guidelines. Complete survey is added as an appendix to this document.
This survey is targeted to get user input for Data Quality and the practices to access and organize Data Quality for CRM and ERP system. This survey will help us to answer our second (RQ2) and third research question (RQ3) on the practicality of DQA methods. Further the outcome of this survey will give us idea about future research prospects in Data Quality Assessment field.
34
3.5.2 Survey planning and design
In our case targeted domain experts are scattered globally and some communication medium was required to gather their input. From different communication methods like email, online meetings, telephone, and physical survey distribution; email was considered the most feasible form of communication. We will use email questionnaire as the main instrument of data generation in this survey. This questionnaire will present a list of possible DQA dimensions identified in literature review to subject matter experts and it will note their feedback in a systematic way. This survey consists of two parts; first part will help to shape the Data Quality view in the organization and second part of this survey will focus on the prioritizations of Data Quality initiatives.
Sampling frame 3.5.2.1
This survey is aimed at a certain audience, the end-users and people implementing ERP and CRM system in the organization under study. The people implementing and maintaining these systems are the ones usually responsible for all the technical aspects of Data Quality. The implementation team can give us more insights into the audit requirements, DQA standardization and organization patterns of software management.
The other set of survey audience, the end users of CRM and ERP systems, are the people directly affected by any quality issue. These end users often set the functional requirements of a system. End user data entry is a vital and first step that incorporates the human intelligence to cleanse and ensure Data Quality. This makes an end-user a vital stakeholder in Data Quality Assessment study.
Table 3 in previous chapter gives a list of job functions we are interested for this study. Each job function is associated with a system that used in their day to day work. Some job functions for instance, the integration experts and finance controllers are working with more than one system in their daily work. Therefore the input from these participants is evaluated for more than one system.
Initially the survey was planned to be distributed to a wider audience, but due to the overlapping dates between the rollout of new ERP system, the audience was limited to just one person of a job function. As there are 10 job functions interesting for this study
35
were identified in the previous chapter, so we selected 10 people each with a separate job function listed in Table 1 to answer this survey.
Although this limitation removed the diversity of the results and input from some important job functions like internal audit was missing, but this study gave us an initial point and we were able to see the organization wide interest in the area of Data Quality and Data Quality assessment.
Questionnaire design 3.5.2.2
This survey is designed to answer two research questions RQ2 (How a method for assessing Data Quality can be defined?) and RQ3 (How well the Data Quality assessment methods work in practice?). Due to a wide spread audience and time zone differences, E-mail questionnaire is the primary strategy of this survey. Survey questionnaire is enclosed as appendix 1 of this study.
The questionnaire is using a mixture of open and closed ended questions with the option for the survey taker to include any dimension or parameter not included in the actual answer template. Questionnaire is started with Data Quality parameters identification then it goes towards more empirical aspects of Data Quality. These empirical aspects will help us to answer RQ3.
In the second part of the survey several dimensions are provided to the survey taker with an illustration of each dimension. The numerical priority provided in this step will make it possible to analyze the importance of Data Quality dimension in relation to the job function answering the questionnaire. This finding will answer the second research question of DQA method.
Survey Design Validation 3.5.2.3
Once the initial survey was designed it was sent to three different team members in the organization for validation. One review was working in Sales operation who works with CRM system on day to day basis. Other reviewer was Director of Systems team who is responsible for overall function of ERP and CRM systems. The last reviewer was an ERP systems Developer who implements the system enhancements in ERP system.
36
After their review survey questions and possible answers were adjusted for better readability, precision of answers and data collection. Initial version of survey was formed as a plain Microsoft Word® Document. Filling of this document was not straight forward for the survey audience. In the light of this review, the survey answers were converted to a click and select fields. This enhancement considerably reduced the survey answering time.
3.5.3 Survey Execution
The survey was distributed via email to all selected participant. The selection of these participants is described earlier in this chapter. Email distribution makes it possible to address globally spread audience and it makes it easy to trace the responses from different audience.
Survey was distributed via email as Microsoft Word® document where drop down lists were used for easy selection. Survey was sent directly to a specified audience so it was easy to track the respondent and the job function of the respondent. Queries from survey participants were entertained via email, instant messengers and voice calls. Finally all ten participants returned the filled questionnaire forms via email. The results of the survey are compiled and discussed in a separate chapter.
3.5.4 Survey limitations
The survey audience was limited to fewer job functions than initially planned audience. That limitation will limit the variation of survey results. Further this survey was executed on a single organization, although this organization is using the latest ERP and CRM systems and is very flexible to adapt the best practices to enhance the overall system quality but more generalization of these results will require conducting this survey across multiple organizations with different organizational structure and CRM and ERP systems used.
3.6 Threats to validity
The validity of a study represents the trust worthiness of the results. Runeson and Höst suggest using four points to view the validity [21].
37
Construct validity is to ensure what we have in mind for this study and what actually
was investigated.
As we are only referring the work published in research journals and books, it is possible to oversee some practices of DQA. The reason for skipping those practices was either the unavailability of implementation details, due to proprietary rights, or the unauthentic marketing nature of published results. So we are only limiting our research to authentically published material.
For survey, it can be a risk if our survey does not focus on answering our research questions or we miss some important aspect in literature review.
Internal validity refers to the validity of relation between a researched fact with a fact
we are researching now. It is a threat that original fact was driven with certain condition while we miss that condition in our study.
Organization wide awareness of Data Quality can be another factor that can enhance the results of this survey. During the survey people were able to realize the importance of Data Quality in the systems but they were not able to fully comprehend those benefits to their job functions.
External validity is concerned with the fact that how generalized our findings can be.
As we are studying a single organization at the moment for this case so it is a possible threat that our findings are specific to the implementation and usage of ERP and CRM system in our organization under study. To overcome this issue we need to extend the audience of this study in future. One possible threat is that survey audience was reduced to one person for each job function. This reduction of the survey participants resulted as the lack of diversity of collected results.
Reliability aspect is concerned that what extent the data and analysis is dependent on
specific researcher. If another researcher performs the same study then the research should not have extreme differences. To overcome this thread we used survey validation and peer review to reduce the preferences of a single researcher.
38
4 Literature Review
This section explores the existing work and narrates the findings of other researchers relevant to this study in the fields of Data Quality and Data Quality Assessment. We will use systematic literature review, described as one of the research method for this study, to answer first research question (RQ1) and gave base to our survey of DQA.
First section in this chapter will show the resultant matrix of literature review conducted for this study. Next we will use literature review to discuss and define DQA. After that DQA method and dimensions are formed with literature review. This section will help us to create the input parameters for our survey. In the end we will conclude with a critical analysis of literature for DQA.
4.1 Literature base for this study
The literature review provided a number of articles for our search of different search keywords. After analyzing all the found literature and filtering any unrelated or redundant literature we are left with following matrix of literature review. Each line in this table presents one literature source and the rationale of selecting this source. For instance Redman [2] was selected because it provides an empirical approach for DQA and it will help us to answer RQ1, and we found Redman [2] using ‘Data Quality’ as keyword of search. Table 3 Literature to research questions mapping will give us literature background to conduct this study. In the next section we will explore different options to answer RQ1 using literature. In the first column search keywords on the top are the source words to extract the corresponding research papers shown in the cells below each keyword. Second column gives the reason to shortlisting this research paper. Research question column shows the contribution of each paper to one or more research questions. For instance the research work by Redman [2] was found with keyword “Data Quality” and it will help us tow answer RQ1.
As described in research methodology chapter 3.4.3, the original table consisted of 62 rows. Using the evaluation method 3.4.6 the table was reduced to following state.
39
Table 3 Literature to research questions mapping Search keywords and associated articles Rationale of selecting this
paper
Research Question this paper supports
Da ta Qu al it y Da ta Qu al it y ass es smen t Da ta Qu al it y m ea su re men t Da ta Qu al it y m an ag emen t Da ta Qu al it y Mo n ito ri n g RQ 1 RQ 2 RQ 3 Redman [2]
Gives a practical aspect of
data quality X
Batini [3]
Data Quality: Concepts, Methodologies and Techniques
X
Loshin [5]
The Practitioner's Guide to
Data Quality Improvement X
Otto [6] Suggests how to measuring
Master Data Quality X
Loshin [7]
Discussion on Master Data
Management X
Fanclanci [8]
Adds user’s satisfaction to
DQA measures. X Freytag [9] Completeness of integrated information sources X Batini [11]
Lists and compares techniques to assess and improve the quality of data
X X
Piprani [12]
Discusses the reasons of
failing DQA X X
Nousak [13]
A Scorecard approach to
improving Data Quality X
Pipino [14] Describes principles to
develop DQA Matrix X X
USAID [15]
Discusses the
implementation of a Data Quality Audit Tool
X
EU DQA[16]
Handbook on Data Quality: Assessment Methods and Tools
40
4.2 Data Quality of CRM and ERP systems
To answer our first research question, to define the Data Quality of CRM and ERP systems, we will start with the definition of Data Quality in general.
4.2.1 Data Quality standing
Data quality is fairly new research area that stands on the intersection of computer sciences, business automations and statistics; as shown below in Figure 4: Research areas related to Data Quality [3, p.17]. These areas expand from more empirical domains like Management Information Systems to more theoretical domains like Knowledge representation. For all these data related fields the quality of data will dictate the outcome of any research or practice. For instance, the results from a Statistical or Data Mining analysis will never be reliable if the data quality of underlying data is not trustworthy. This illustration puts Data Quality at the center of all data related activities. [3][9]
Figure 4: Research areas related to Data Quality [3, p.17]
In following text we briefly examine each of the domains mentioned in the figure 4 and the relationship of Data Quality to this domain.
Data Integration ensures that data across multiple data sources stays synchronized. For the case of this study, the data in ERP system is fed from the CRM system using Integration processes. If the data quality in one system is
41
not of high quality or if the integration process has some flaws then we can never ensure the data quality in ERP system. So Data Integration has very high influence on Data Quality and vice versa.
Data mining is the study of extracting as much meaningful information to solve a problem at hand from existing data as possible. If the Data Quality of original data is not very good then results of Data Mining cannot be trustworthy.
Statistics and Statistical data analysis is domain similar to data mining where scientific methods are used to extract inferences from underlying data. Poor quality of source data will result in poor statistical inferences.
Knowledge representation is the study of presenting the information in a meaningful way according to given context. The quality of underlying data will directly translate to the quality of end results by knowledge representation.
Management Information System (MIS) is the study of engineering system to support and maintain management and business processes. Poor Data Quality in MIS will lead to poor business decision making.
4.2.2 Method of DQ definition selection
Most of the Data Quality definitions directly translate the Data Quality to a single true version of information [9]; but this definition does not consider the fact that data is subjective [5]. For instance a CRM system will collect customer information with relation to the sales department. Examples of sales customer data can be probability of securing a deal with customer, contact persons at the customer site and their connection preferences. At the same time an ERP system will need customer information to track organization resources for example customer billing address, quantity of items sold, payment method. If customer data is collected and organized with keeping a single system in mind, it will not be of high quality to all systems. The data is generated by the business processes responsible to collect relevant information, so we cannot expect a database that compensates the flaws in a business process.
By the help of literature review we are able to comprehend that most organizations measure data quality in the order of 1) completeness of information 2) data life cycle



![Figure 3: Literature review process [17] diagram shows different steps of literature review presented by Oates [17]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/5dokorg/4194998.91618/29.918.130.788.346.636/figure-literature-review-process-diagram-different-literature-presented.webp)
![Figure 4: Research areas related to Data Quality [3, p.17]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/5dokorg/4194998.91618/40.918.264.676.514.836/figure-research-areas-related-data-quality-p.webp)